Figure 8. The individual effects of propranolol, guanethidine and capsaicin on slow hyperpolarizations recorded from choroidal arterioles.
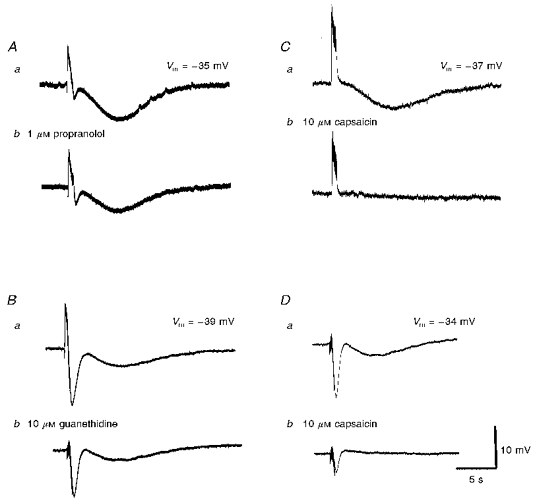
A series of membrane potential changes, initiated in the presence of phentolamine (1 μM) by trains of high-frequency nerve stimuli (supramaximal voltage, 50 μs, 50 Hz, 1 s) are shown. The slow hyperpolarization was reduced in amplitude by each of propranolol (1 μM; Ab) and guanethidine (10 μM; Bb) and abolished by capsaicin (10 μM; Cb). The traces shown in D were recorded in the presence of guanethidine (10 μM); Db, the guanethidine-resistant component was virtually abolished by capsaicin. A, B, C and D were recorded from 4 different cells. Aa, Ba, Ca and Da are respective control responses. The scale bars on the right refer to all traces. Vm refers to resting membrane potential.
