Figure 9. The effects of apamin, charybdotoxin and glibenclamide on two distinct hyperpolarizations recorded from choroidal arterioles.
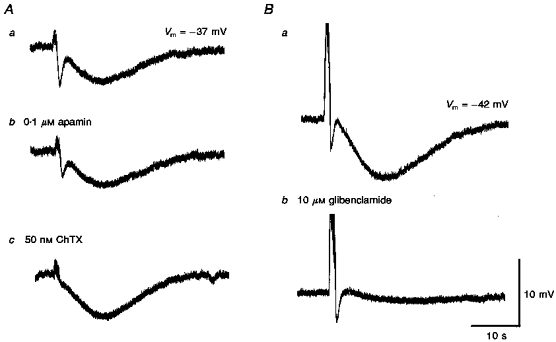
A comparison of the effects of apamin (0.1 μM) alone (Ab) and with charybdotoxin (ChTX, 50 nM; Ac) each in the presence of guanethidine (10 μM) and of glibenclamide (Glib, 10 μM) in the presence of phentolamine (1 μM) on the responses of guinea-pig choroidal arterioles to trains of field stimulation (supramaximal voltage, 50 μs, 50 Hz, 1 s). A and B were recorded from 2 different cells. Respective controls Aa and Ba were in the presence of guanethidine and phentolamine. Ab, cholinergic IJP but not slow hyperpolarization was inhibited by apamin. Ac, subsequent addition of ChTX abolished the residual IJP and enhanced the amplitude of the slow hyperpolarization. Bb, glibenclamide almost completely inhibited the slow hyperpolarization without affecting IJP. The scale bar on the right refers to all traces. Vm refers to resting membrane potential.
