Figure 7. Effect of different protein kinase inhibitors on TRH-induced modification of HERG deactivation kinetics.
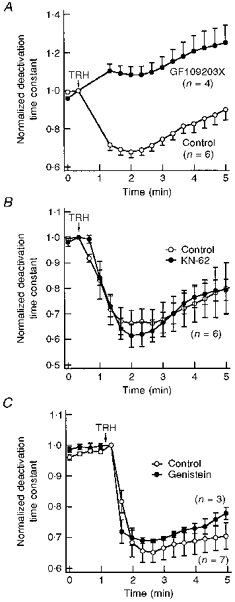
A, blockade of the TRH effect by the PKC inhibitor GF109203X. Deactivation time constants normalized to that measured at the moment of TRH addition are shown for untreated oocytes (control) or oocytes incubated for 4–6 h with 10 μM GF109203X. Test pulses were delivered to the cells every 20 s. Time constant values for the two pulses following introduction of TRH into the chamber have been deleted for clarity. The start of a 30 s perfusion with medium containing 1 μM TRH is indicated. B, TRH-induced effects in the presence of the Ca2+-calmodulin protein kinase II inhibitor KN-62. Variations in the deactivation time constant for untreated oocytes (control) and oocytes incubated for 1–3 h with 20 μM KN-62 are shown. The start of a 30 s perfusion with medium containing 1 μM TRH is indicated at the top of the graph. C, TRH-induced effects in the presence of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein. Normalized deactivation time constant values are shown for oocytes injected with a micropipette filled with 100 μM genistein (final intracellular concentration approximately 5 μM genistein) or vehicle (control) 30 min before start of HERG current recordings. The start of perfusion with 1 μM TRH is indicated. In this case, the hormone remained present up to the end of the experiments.
