Figure 6. Effect of adenosine on caffeine-induced Ca2+ transient.
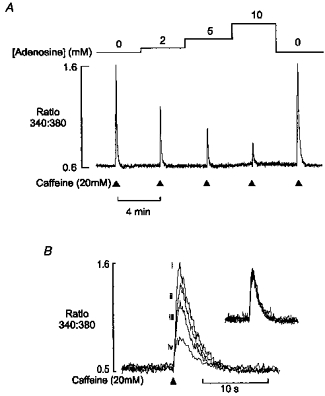
A, continuous record of the 340 nm/380 nm fluorescence ratio from a saponin-permeabilized fibre in the presence of 100 nm Ca2+ and 5 mm ATP. Caffeine (20 mm) was briefly applied at 4 min intervals as indicated. Following an initial steady-state control response, the adenosine concentration was increased in a stepwise manner from 2 to 10 mm. This resulted in a corresponding decrease in the amplitude of the caffeine-induced Ca2+ transient. Removal of adenosine resulted in a rapid return to control levels. B, superimposed Ca2+ transients from the same preparation, in the presence of (i) 0, (ii) 2, (iii) 5 and (iv) 10 mm adenosine. Normalized responses (inset) show that the time course of the Ca2+ transient was unaffected.
