Figure 2. Two types of firing pattern in the superior salivatory neurones.
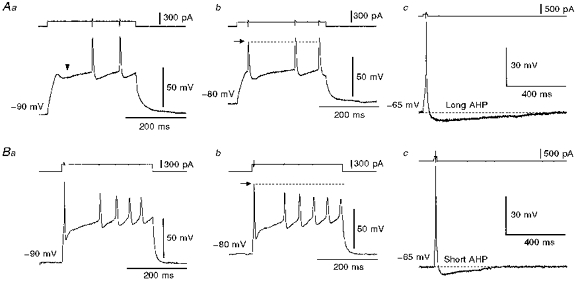
A, a neurone labelled from the chorda-lingual nerve displayed late (a) and interrupted (b) spiking patterns in response to injections of long depolarizing current pulses applied at membrane potentials of −90 and −80 mV, respectively. The arrowhead (a) indicates a hyperpolarizing notch. This neurone showed a long after-hyperpolarization (AHP) near its resting membrane potential (c). B, a neurone labelled from the tongue displayed the interrupted spiking pattern at membrane potentials more hyperpolarized than −80 mV (a and b). This neurone showed a relatively short after-hyperpolarization near its resting membrane potential (c).
