Figure 1. Anatomy and physiology of opponent and non-opponent pathways in the primate retina.
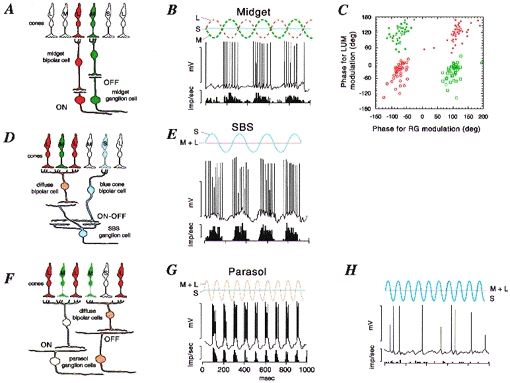
A, midget pathway. Schematic view of a vertical section through the parafoveal retina. Midget bipolar cells contact a single cone photoreceptor and provide excitatory input to midget ganglion cells. Each L and m cone makes contact with both an on-centre and an off-centre midget bipolar cell; only one example of each is drawn for clarity. B, response of a ‘green-on’ midget cell. The intracellular response and averaged spike discharge rate are shown below a schematic representation of the cone modulation due to the stimulus (red-green modulation). The cell responds to increases in m cone activation but is inhibited by L cones. C, 4 subclasses of red-green opponent cells can be distinguished on the basis of their response to achromatic (LUM) or red-green chromatic (RG) modulation at 4 Hz. Open red circles, red-on; filled red circles, red-off; open green squares, green-on; filled green squares, green-off. The phase of cell response is shown relative to the phase of the stimulus; negative phase representing increasing response lag relative to the stimulus. D and E, the SBS (blue-on) pathway. SBS cells receive excitatory (on) input from the blue cone-contacting bipolar cell, and excitatory (off) input from an off-centre diffuse bipolar cell. They respond vigorously to S cone modulation. F, parasol cells receive excitatory input from diffuse (on- or off-centre) bipolar cells, which contact both L and m cones and hence are non-opponent. The response of an off- parasol cell is shown in G. This cell responds to combined modulation of L and m cones, but is unaffected by a stimulus (shown in H) which modulates selectively the S cones. Panels B, E, G and H are modified from Dacey & Lee (1994). Panel C is modified from Lankheet et al. (1998). Calibration values for B, E, G and H are 50 mV and 400 impulses s−1.
