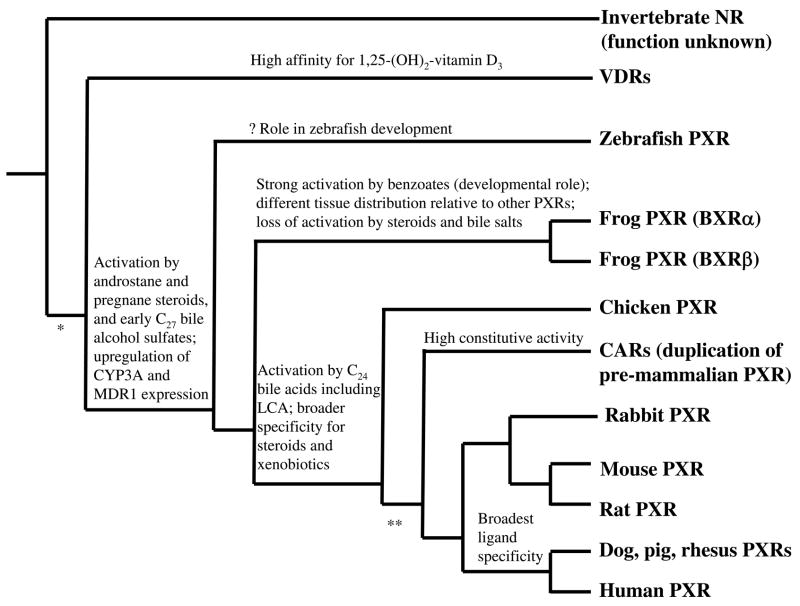
Figure 3. Proposed phylogeny of PXRs showing functional characteristics.
The phylogenetic tree is derived from known phylogenetic relationships of the animal species integrated with tissue expression patterns and pharmacological properties. Characteristics included are tissue expression pattern; activation by pregnane steroids, androstane steroids, C27 bile alcohol sulfates (representative of the earliest bile salts to evolve in vertebrates), C24 bile acids (such as cholic acid and lithocholic acid, LCA); ability to upregulate expression of CYP3A and MDR1; and high constitutive activity. * and ** indicate proposed times when gene duplication occurred leading to expansion of the NR1I subfamily (that currently includes PXR, VDR, and CAR) when one of the duplicated genes diverged and took on different functions. An ancestral gene is thought to have duplicated in early vertebrate evolution, ultimately resulting in separate VDR and PXR genes (*). Just prior to or early in mammalian evolution, the PXR gene is thought to have duplicated (**); subsequent divergence of one of these genes resulted in the CAR gene.