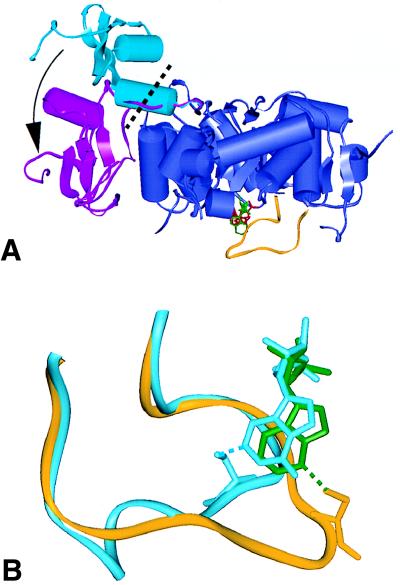
Figure 2.
(A) Comparison of flanking domain positions in the human (magenta) and hamster (cyan) (32) complexes. The two conformations are related by a rotation (arrow) about a vector through the hinge region (dotted black line). Flanking domains are 75% and 44% complete in the human and hamster models, respectively. Also shown are the core domain (blue), active site loop (yellow), and ligands (red and green). (B) Comparison of the active site loop observed in the human (yellow) and hamster (cyan) complexes. Purine rings for IMP (cyan) and 6-Cl-IMP (green) are shown. The IMP C2-Cys-331 adduct (cyan dotted line) seen in the hamster complex (32) is replaced by a C6-Cys-331 adduct here (green dotted line). This displaces the loop (yellow) to the opposite side of the purine ring.