Abstract
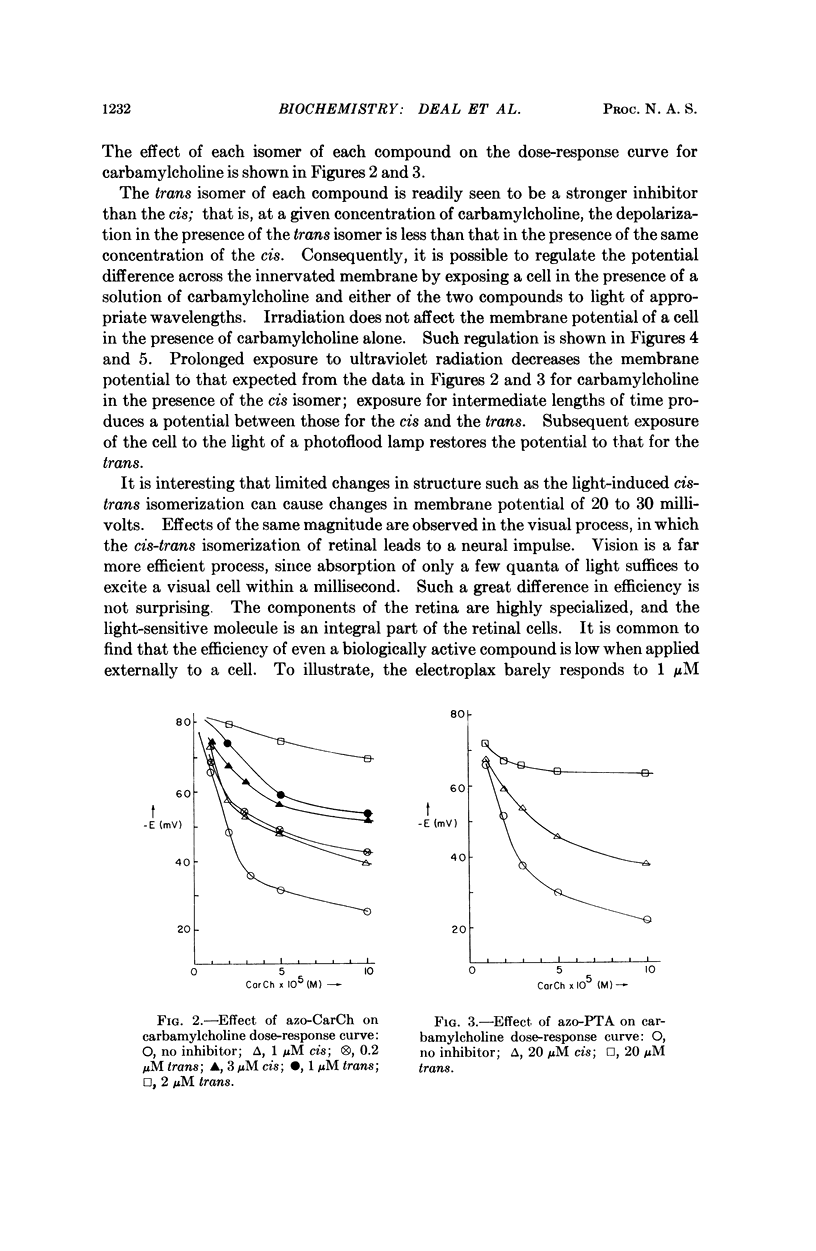
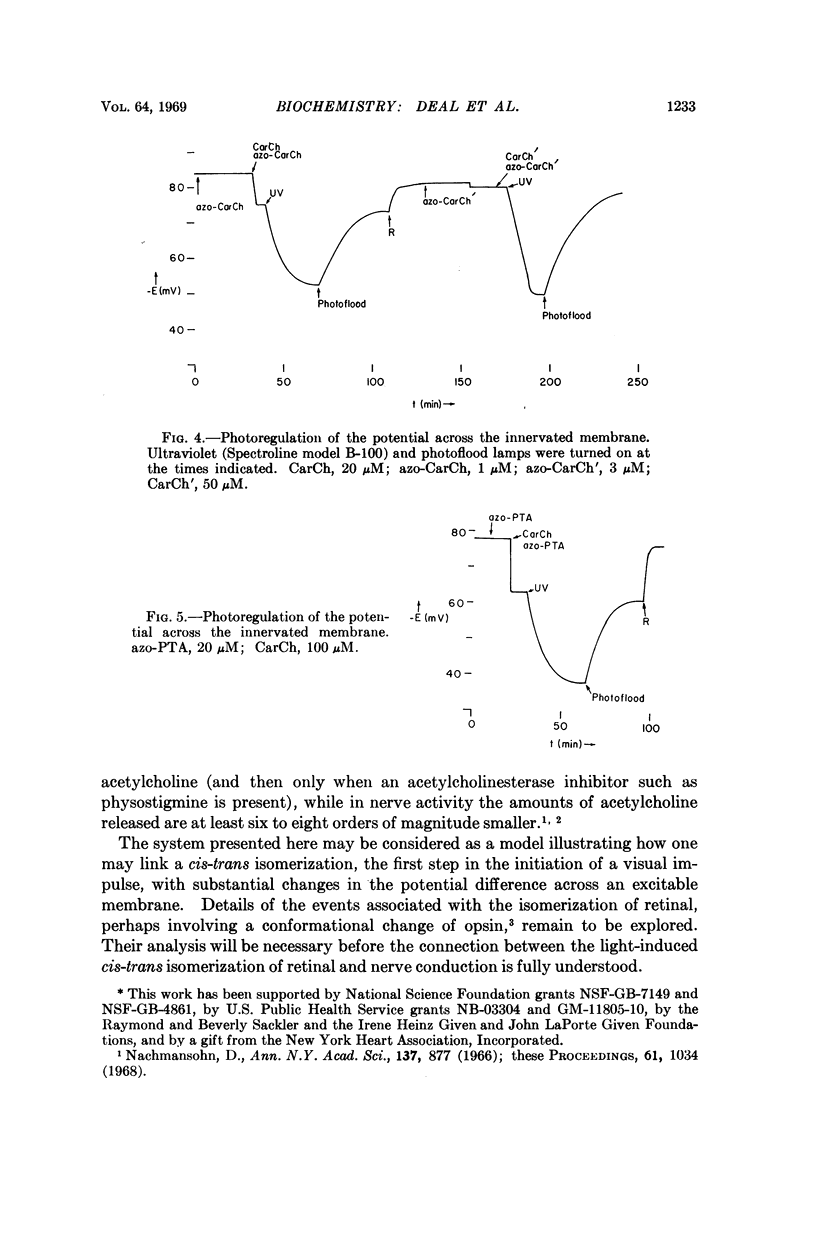
The photochromic compounds N-p-phenylazophenyl-N-phenylcarbamylcholine chloride and p-phenylazophenyltrimethylammonium chloride inhibit the carbamylcholine-produced depolarization of the excitable membrane of the monocellular electroplax preparation of Electrophorus. The trans isomer of each predominates in the light of a photoflood (420 mμ) lamp; they are stronger inhibitors than the cis isomers, which predominate under ultraviolet (320 mμ) irradiation. The potential difference across the excitable membrane may be photoregulated by exposing an electroplax in the presence of a solution of carbamylcholine and either of the two compounds to light of appropriate wavelengths, since light shifts the cis-trans equilibrium. The system may be considered as a model illustrating how one may link a cis-trans isomerization, the first step in the initiation of a visual impulse, with substantial changes (20-30 mv) in the potential difference across an excitable membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieth J., Vratsanos S. M., Wassermann N., Erlanger B. F. Photoregulation of biological activity by photocromic reagents. II. Inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1103–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGMAN H. B., PODLESKI T. R., BARTELS E. CORRELATION OF MEMBRANE POTENTIAL AND POTASSIUM FLUX IN THE ELECTROPLAX OF ELECTROPHORUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:138–150. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman H., Vratsanos S. M., Erlanger B. F. Photoregulation of an enzymic process by means of a light-sensitive ligand. Science. 1968 Dec 27;162(3861):1487–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3861.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmansohn D. Chemical control of the permeability cycle in excitable membranes during electrical activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):877–900. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E., NACHMANSOHN D. An isolated single electroplax preparation. I. New data on the effect of acetylcholine and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. Molecular basis of visual excitation. Science. 1968 Oct 11;162(3850):230–239. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3850.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



