Figure 1.
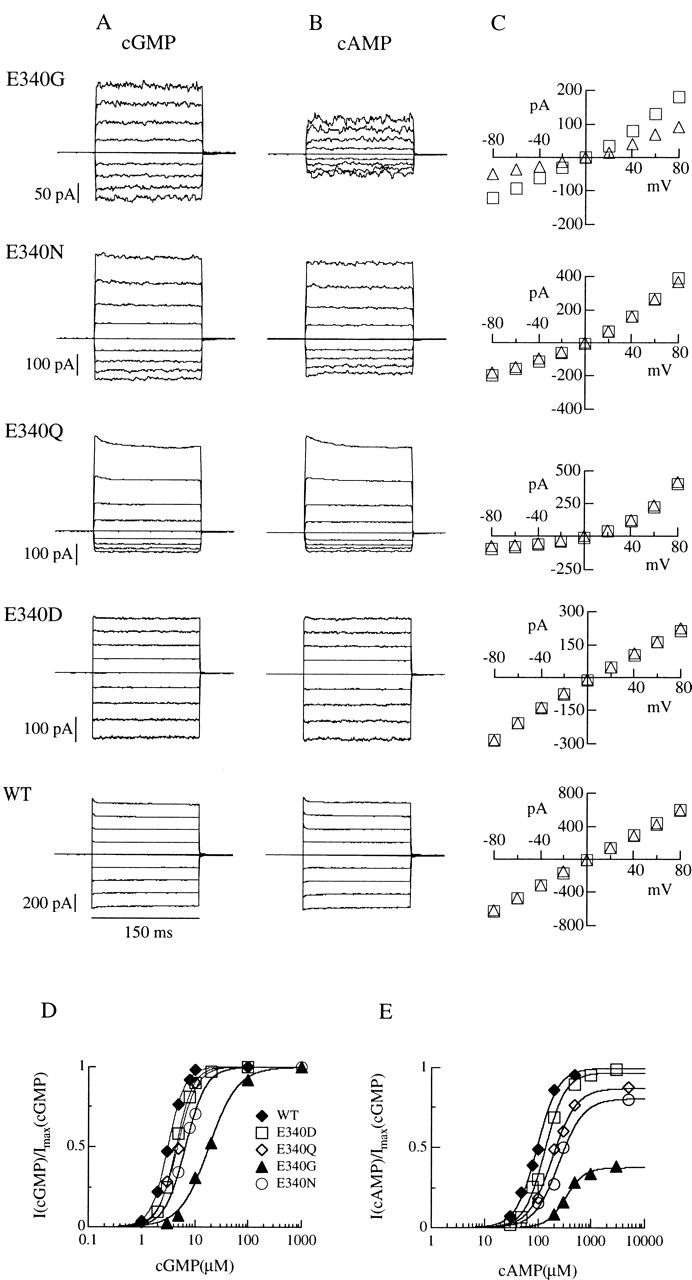
Maximal currents activated by cGMP or cAMP for wild-type and mutant olfactory CNG channels. Currents in each row were from the same excised inside-out patch. Voltage steps of 150-ms duration from a holding potential of 0 mV were given from −80 to +80 mV in 20-mV steps. Currents were activated by cyclic nucleotide concentrations eliciting maximal currents (see dose–response relations in D–E): (A) cGMP concentration was 1 mM, (B) cAMP concentration was 3 mM for E340G and E340D, 5 mM for E340N and E340Q, and 500 μM for wild-type channels. (C) Current–voltage relations from recordings shown in A and B for cGMP (□) and cAMP (▵). (D–E) Dose–response relations. Currents activated by cGMP or by cAMP at −80 mV were measured in the same patch, normalized to the maximal current activated by cGMP at −80 mV, and plotted versus cGMP (D) or cAMP (E) concentrations. Continuous lines represent the best fit of the Hill equation () to the data with the following values. Wild-type: I max,cA/I max,cG = 0.99, K 1/2,cG = 3.2 μM, n cG = 2.7, K 1/2,cA = 97 μM, n cA = 2.2; E340D: I max,cA/I max,cG = 0.97, K 1/2,cG = 4.5 μM, n cG = 2.7, K 1/2,cA = 137 μM, n cA = 2.3; E340Q: I max,cA/I max,cG = 0.87, K 1/2,cG = 4.8 μM, n cG = 2.4, K 1/2,cA = 189 μM, n cA = 2.0; E340N: I max,cA/I max,cG = 0.81, K 1/2,cG = 6.6 μM, n cG = 2.3, K 1/2,cA = 251 μM, n cA = 1.9; E340G: I max,cA/I max,cG = 0.37, K 1/2,cG = 18.5 μM, n cG = 1.6, K 1/2,cA = 335 μM, n cA = 2.5.
