Figure 7.
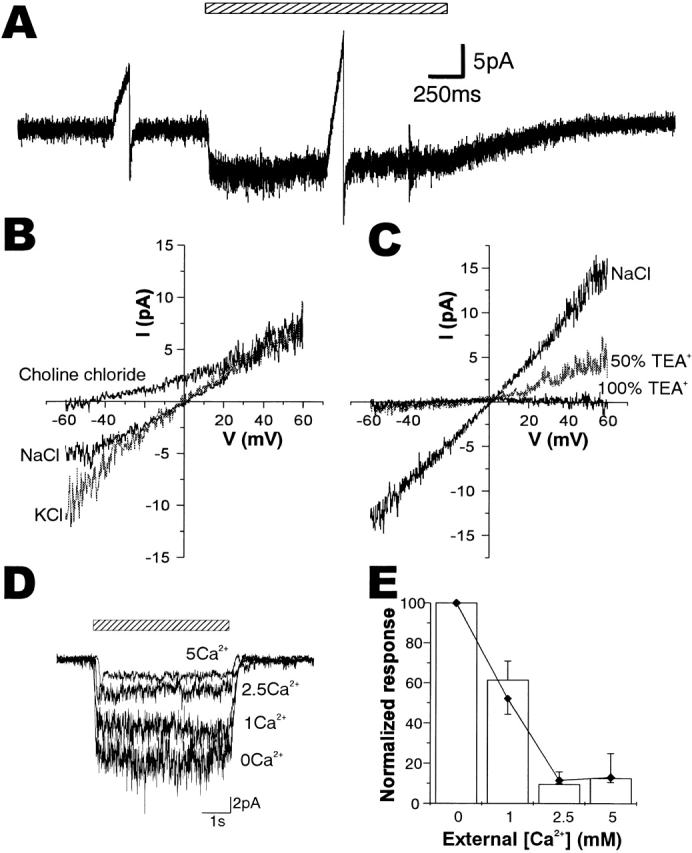
Ionic properties of sucrose-activated channels in the outside-out patches. (A) A sucrose-induced current record of an outside-out patch voltage clamped at −60 mV, in which two voltage ramps from −60 to +60 mV were inserted in the period of steady sucrose-induced current (right) and in the control period without sucrose application (left). (B) I-V relationships of the ensemble current induced by 250 mM sucrose obtained from the current traces responding to voltage ramps from −60 to +60 mV in the external Ca2+-free Ringer (NaCl) and in solutions in which Na+ was replaced by K+ (KCl, gray trace) and choline+ (choline chloride). The trace of NaCl was obtained from the record shown in A. (C) I-V relationships in external solutions in which NaCl was half (50% TEA+, gray trace) or fully (100% TEA+) replaced by TEA chloride. TEA+ blocked sucrose-activated channels from the extracellular side both inwardly and outwardly. (D) Inhibition of sucrose-induced currents by Ca2+ in the stimulant solution. Current traces induced by 250 mM sucrose on an outside-out patch in various concentrations of Ca2+ (given in millimolar) are shown. The period of stimulation is shown by a shadowed bar. (E) A plot of responses against Ca2+ concentration. Relative magnitude of conductances activated by 250 mM sucrose with voltage ramps from −60 to +60 mV (n = 3, open bars) and the variances of current fluctuations at −60 mV(♦) in various Ca2+ concentrations. SEMs are shown by vertical lines above (conductances) or below (variances) the data points.
