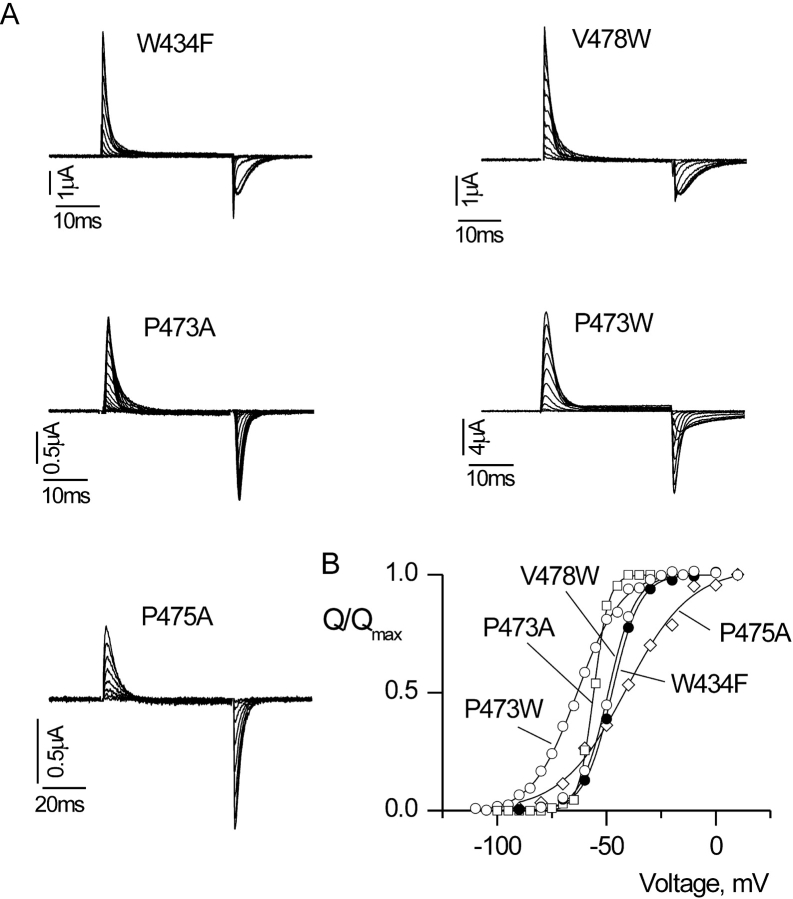
Figure 3.
Gating currents and Q-V relations for Shaker Kv channels with nonconducting phenotypes. (A) Families of gating current records for W434F and four other nonconducting mutant Shaker channels. In all cases, membrane voltage was depolarized to various test voltages and then repolarized to the holding voltage. For W434F, holding voltage was −90 mV and depolarizations were from −90 to 0 mV, in 10-mV increments. For V478W, holding voltage was −90 mV and depolarizations were from −80 to 20 mV, in 10-mV increments. For P473A, holding voltage was −100 mV and depolarizations were from –100 mV to −5 mV, in 5-mV increments. For P473W, holding voltage was –110 mV and depolarizations were from −110 to −20 mV, in 10-mV increments. For P475A, holding voltage was −100 mV and depolarizations were from −100 to 0 mV, in 10-mV increments. A P/−4 protocol was used to subtract leak and linear capacitive currents. (B) Normalized Q-V relations for W434F and three other nonconducting mutant Shaker channels. Q was obtained by integrating both the ON and OFF components of gating current, taking their average and normalizing to Qmax measured at depolarized voltages. Smooth curves are single Boltzmann fits to the data with parameters as follows: W434F: V50 = −47.1 mV, z = 4.1; P473W: V50 = −64.1 mV, z = 2.5; P473A: V50 = −55.9 mV, z = 7.0; V478W: V50 = −48.6 mV, z = 4.1; P475A: V50 = −41.1 mV, z =1.7.