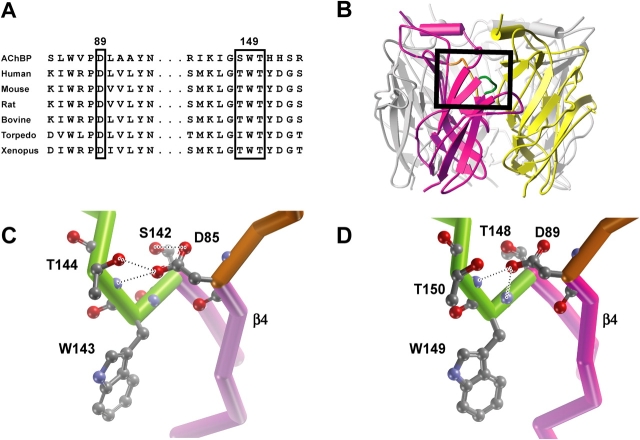
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment and relationship between recognition domains A and B in AChBP and our structural model of receptor ligand binding domain. (A) Alignment of local regions of AChBP and α subunits from different species. (B) Mutagenesis-based homology model of the human muscle receptor ligand binding domain (Sine et al., 2002a). The α subunit is highlighted in magenta and ɛ subunit in yellow, with the remaining subunits in gray. The box encloses recognition domains A (orange) and B (green) of the α subunit. Close up views of the box in B for AChBP (C) and receptor (D) with side chains of key residues rendered in ball and stick representation. Structures in C and D are views from inside the central vestibule. Dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds with the following distances. AChBP: D85 oxygen1 to T144 hydroxyl, 2.7 Å; D85 oxygen1 to T144 main chain amide, 2.9 Å; D85 oxygen2 to S142 hydroxyl, 2.6 Å. Receptor: αD89 oxygen1 to αW149 main chain amide, 2.7 Å; αD89 oxygen1 to αT150 main chain amide, 2.5 Å.