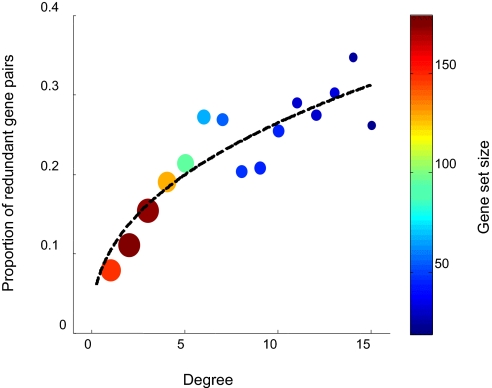
Fig. 5.
Proportion of functionally redundant duplicate pairs in a literature curated dataset as a function of their connectivity in the protein interaction network. The data for the analysis consisted of a list of 766 duplicate-gene pairs selected by a sequence similarity criterion (BLAST e value <3 × 10−108). Each of these pairs was subjected to a manual literature examination in search of evidence for functional redundancy. This procedure resulted in 112 redundant pairs. At each degree connectivity, the value at the y axis denotes the fraction of genes with that degree that have an annotated redundant paralog in the set of 112 pairs. Proportions were calculated by normalizing to the total set of curated paralogs, thus avoiding potential biases associated with literature over-representation of highly connected proteins. Both color and size of the data points represent the number of genes in a given category (colors specified by the color bar at Right). Analysis was performed by applying a sliding window of width = 2 on the degree axis.