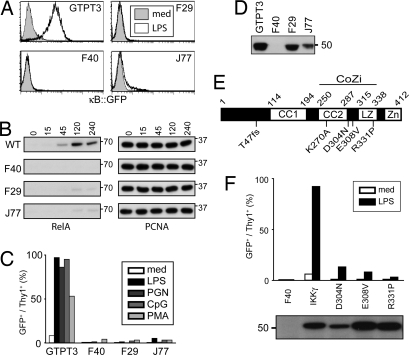
Fig. 1.
Defect in NF-κB signaling in F40, F29, and J77 cells due to mutations in IKKγ. (A) Cells were stimulated for 24 h with 1 μg/ml LPS before analysis for NF-κB-dependent GFP expression. (B) Nuclear extracts from cells stimulated with 10 μg/ml LPS and probed for RelA and PCNA. (C) Cells stimulated for 24 h with 1 μg/ml LPS, 10 μg/ml PGN, 250 nM CpG DNA, or 50 ng/ml PMA/1 μM Ionomycin analyzed for NF-κB-dependent GFP and Thy1 expression by flow cytometry. (D) Cell lysates were probed for IKKγ. (E) Secondary structure of IKKγ (CC1, coiled coil 1; CC2, coiled coil 2; LZ, leucine zipper; Zn, zinc finger). F40 carries a frame shift (T47fs). F29 and J77 contain point mutations (E308V and R331P, respectively). D304N occurred in a patient with EDA-ID. K270A is a designed mutation. (F) F40 cells complemented with the indicated IKKγ alleles. Cells stimulated for 24 h with 1 μg/ml LPS were analyzed for NF-κB-dependent GFP expression. Lysates were probed for AU1-tagged IKKγ.