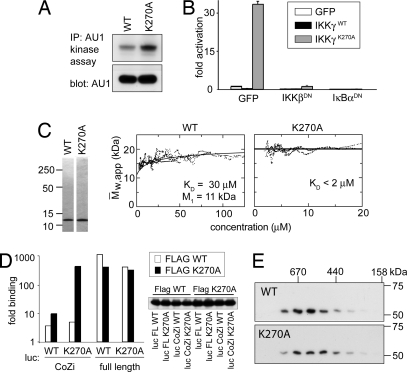
Fig. 5.
K270A causes high-affinity CoZi interactions. (A) GTPT3 cells were transduced with the indicated IKKγ alleles. AU1-tagged IKKγ was precipitated, and a kinase assay was performed with GST-IκBα (amino acids 1–100) as a substrate. The expression level of AU1-tagged IKKγ in lysates was analyzed. (B) NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity in 293 cells 48 h after transfection with the indicated combinations of plasmids. IKKβDN corresponds to IKKβK44A and IκBαDN indicates to IκBαS32A+S36A. (C) (Left) CoZiWT and CoZiK270A were purified from E. coli. (Right) Mass-action-driven association was analyzed by analytical ultracentrifugation. Plots are from sedimentation equilibrium runs and indicate the formation of dimers. The Kd value for 30 ± 5 μM CoZiWT and the monomer size as determined from fitting the raw data are indicated. The latter is in excellent agreement with the theoretical value (10.9 kDa). CoZiK270A did not dissociate detectably at concentrations as low as 2 μM and showed only dimer (Mw, app, weight average apparent molecular weight). (D) The 293 cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of luciferase-tagged IKKγ (full length or CoZi) and FLAG-tagged IKKγ (only full length) either wild type or mutant in position 270. Proteins were precipitated with an antibody against Flag and eluted with Flag peptide. The ratio between luciferase activity in eluates and lysates is shown. The expression of Flag-tagged proteins was analyzed by Western blot. (E) Lysates from F40 cells transduced with IKKγWT or IKKγK270A were fractionated over Superdex 200. Fractions were tested for IKKγ.