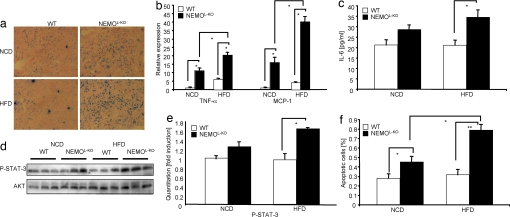
Fig. 3.
Massive macrophage infiltration into livers of NEMOL-KO mice leads to up-regulation of proinflammatory cytokines, induction of cell death and compensatory proliferation. (a) Immunohistochemistry of liver cryostat sections of control and NEMOL-KO mice using F4/80 antibody to detect infiltrating macrophages. (b) Relative expression of MCP-1 and TNF-α in livers of control and NEMOL-KO mice on NCD and HFD was determined by real-time PCR using TaqMan Assay (n = 8 per genotype). (c) Evaluation of IL-6 levels was performed by ELISA from sera of control and NEMOL-KO mice on NCD and HFD at 16 weeks of age. (d) Representative Western blots of liver protein lysates from control and NEMOL-KO mice on NCD and HFD using the indicated antibodies (n = 3 per genotype). (e) Quantitation of P-STAT-3 intensities from Western blots shown in d by using Quantity one software. (f) Determination of apoptosis by TUNEL staining of livers of control and NEMOL-KO mice was expressed as percentage of total cells. TUNEL-stained liver sections were counterstained with DAPI and from five exemplary sections (see SI Fig. 7) for each value DAPI as well as TUNEL-positive cells were counted (n = 5 per genotype). Values are mean ± SEM. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.001 vs. control.