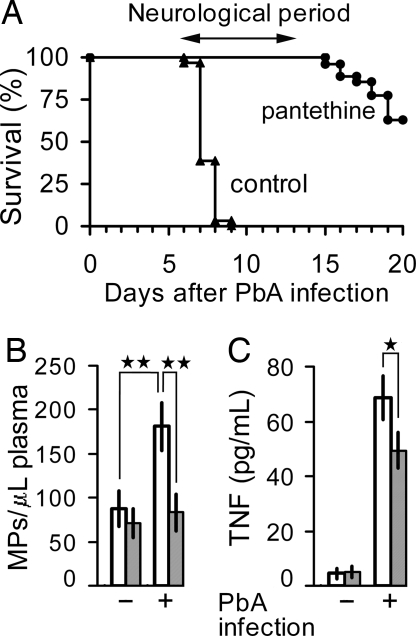
Fig. 1.
Prevention of the cerebral syndrome by pantethine treatment in PbA-infected mice. (A) cumulative survival analysis of infected CBA/J mice, either treated or not treated with pantethine. Control mice received saline injections (n = 31). Death in this group was due to cerebral complications. The syndrome did not occur in pantethine-treated animals. The treatment consisted in daily i.p. injections of either 30 mg of pantethine, starting on day 1 after infection (n = 20), or 5 mg, starting 8 days before infection (n = 7). The two treated groups are combined in the graph. Beyond the neurological phase, surviving mice died from hyperparasitemia with consequent severe anemia, without cerebral syndrome. (B and C) plasma MP and TNF levels on day 7 after infection in control and treated mice (n = 10 in each group). Open bars, untreated; hatched bars, pantethine treatment. +, infected; −, noninfected. Results are expressed as means ± SD; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.