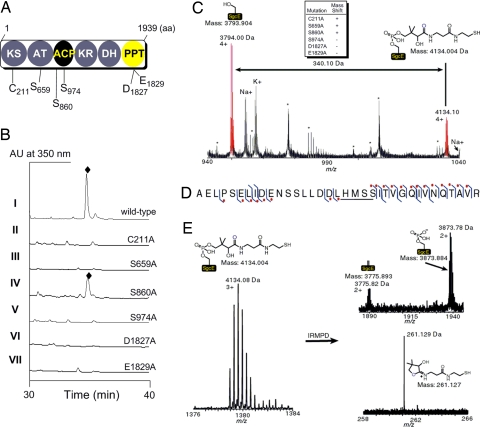
Fig. 2.
Functional assignments of SgcE. (A) Putative domain organization of PKSE and the amino acids of SgcE targeted for site-directed mutagenesis. (B) HPLC traces of C-1027 (♦) production from SB1005 using complementation plasmids expressing wild-type SgcE (pBS1049, I); C211A (pBS1064, II); S659A (pBS1069, III); S860A (pBS1070, IV); S974A (pBS1071, V); D1827A (pBS1071, VI); and E1831A (pBS1072, VII). (C) ESI-FTICR-MS analysis of the ACP-containing peptide fragment of heterologously produced SgcE indicating a + 340.1 Da mass shift consistent with the 4′-phospopantetheine (4′-PP) cofactor. Upper Center indicates whether a similar mass shift is observed for the indicated SgcE mutation. The asterisks (*) refer to peptides that are not the ACP active site, and Na+ and K+ are sodium and potassium adducts of the corresponding peptides. (D) Peptide ion subjected to collisionally activated dissociation. The right hook indicates that a b-fragment ion was identified and the left hook indicates that a y-fragment ion was identified. The red dot denotes fragment ions that contain the 340.1 Da modification. The location of the 340.1 Da modification is underlined. (E) Characteristic mass spectral pattern upon 4′-PP elimination as shown for SgcE. IRMPD, infrared multiphoton dissociation.