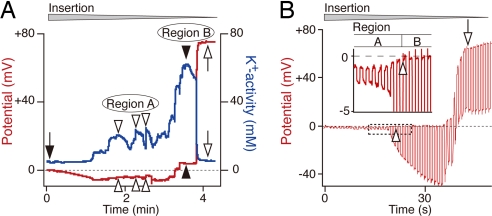
Fig. 2.
Electrochemical properties of compartments in the lateral cochlear wall. (A) A recording of the potential (red) and aK+ (blue) with a double-barreled K+-selective electrode driven through the lateral wall commences with the electrode in perilymph (filled arrow). Open and filled arrowheads, respectively, point to the two regions that exhibit different profiles. After encountering the distinct profiles of Regions A and B, the electrode reached the IS (open arrows). In this and subsequent recordings, the wedge above the trace indicates the period during which the electrode was advanced. (B) A single-barreled electrode made simultaneous measurements of the potential and input resistance in the lateral wall. The electrode was driven through the lateral wall while being stimulated by constant current pulses (25-nA/pulse, duration 400 msec). At the point where the potential became slightly positive (open arrowheads), the input resistance increased greatly; this combination signaled entry from perilymph in Region A into the inside of the syncytium, Region B. Boxed area is enlarged in Inset. Further insertion of the electrode resulted in detection of the regions showing highly positive potential with high input resistance (open arrow), which might represent the feature of the IS fluid or MCs.