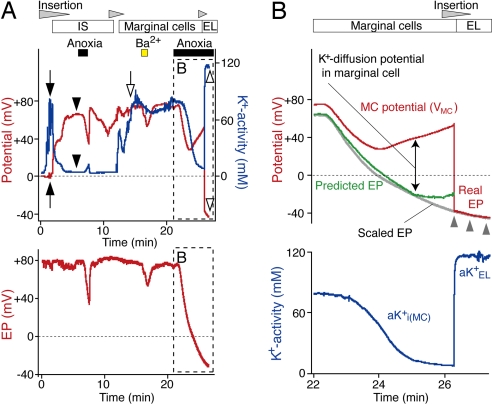
Fig. 5.
Identification of MCs and analysis of their properties. (A) A K+-selective electrode (Upper) advanced from the perilymph first encountered the syncytium (filled arrows) and the IS (filled arrowheads) toward the endolymph. Anoxia was imposed briefly when the electrode was in the IS. Entry into the MCs was signaled by a highly positive potential and elevated aK+ (open arrow). Ba2+ (1 mM) and anoxia were tested while the electrode was held at that location. The electrode was ultimately inserted into the endolymph during a period of anoxia (open arrowheads). Throughout the experiment, the EP was recorded with a second electrode (Lower). (B) The EP during anoxia was predicted (green) with the equation, EP = VMC + (RT/F) ln(aKi(MC)+/aKEL+). The potential (VMC, red) and intracellular aK+ (aKi(MC)+, blue) of MCs and the endolymphatic aK+ (aKEL+) were obtained from A (Upper, box and open arrowhead). The vertical scale of the EP in A (Lower, box) was adjusted (scaled EP, gray line) to fit the curve of the potential that was recorded by the K+-selective electrode when it was in endolymph (red line highlighted by gray arrowheads).