Figure 3. Toca-1 Recruitment to the Vicinity of Intracellular S. flexneri Is Independent of IcsA and N-WASP.
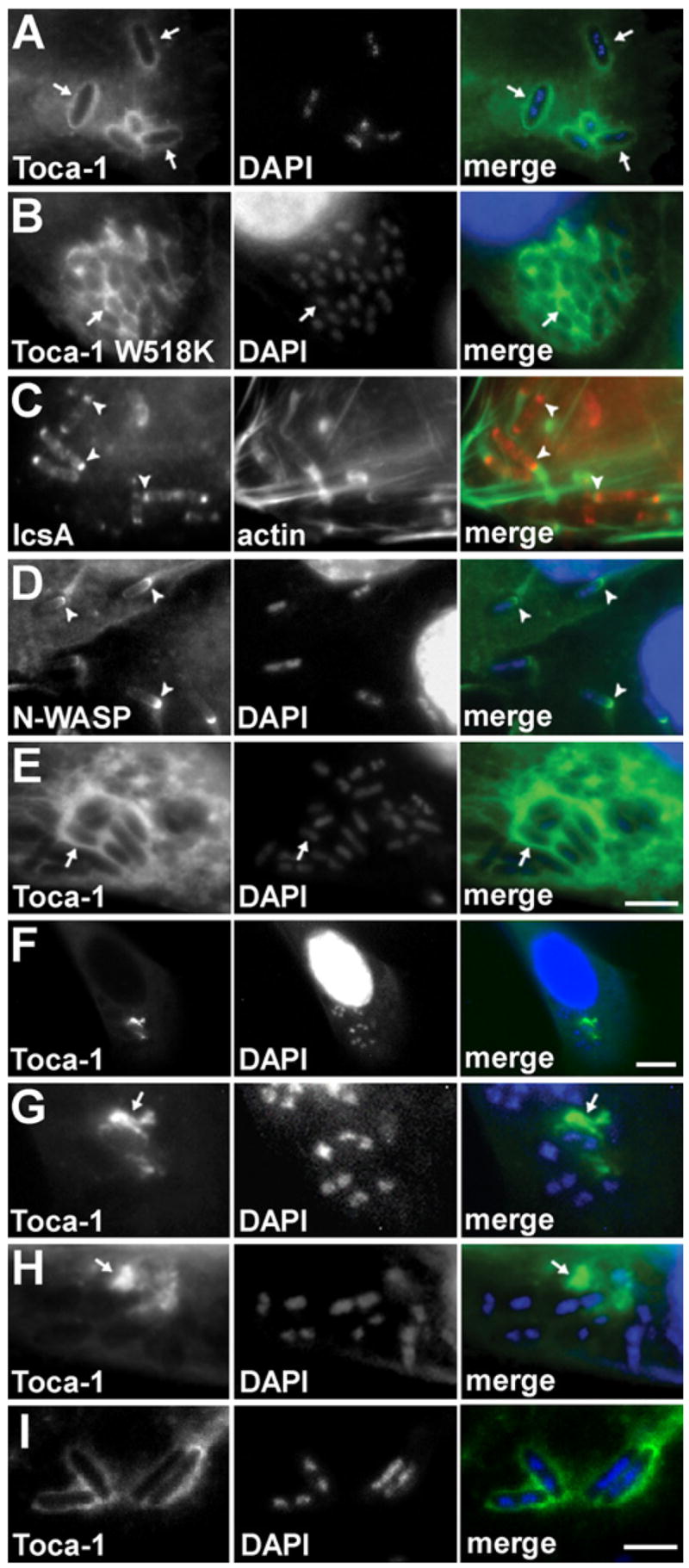
Wild-type (A–D, F, and G), icsA (E and H), or virA (I) S. flexneri with wild-type Toca-1 (A and C–I) or Toca-1 W518K (B) localized around the bacteria inHeLa cells (which are N-WASP+/+, [A]–[E] and [I]) or in N-WASP−/− fibroblast-like cells (F–H). IcsA ([C], arrowheads, red) or N-WASP ([D], GFP-N-WASP, arrowheads, green) localized to one end of the bacteria. Note more diffuse localization of Toca-1 around bacteria in N-WASP−/− cells (F–H). Green, GFP-Toca-1 or GFP-Toca-1 W518K (arrows) (A, B, and E–I), actin (C), or GFP-N-WASP (D). Red, immunofluorescent labeling of IcsA (C). Blue, fluorescent labeling of bacterial and cellular DNA with DAPI. Scale bars: (A)–(E), shown in (E), 5 μm; (F), 15 μm; (G)–(I), shown in (I), 4 μm.
