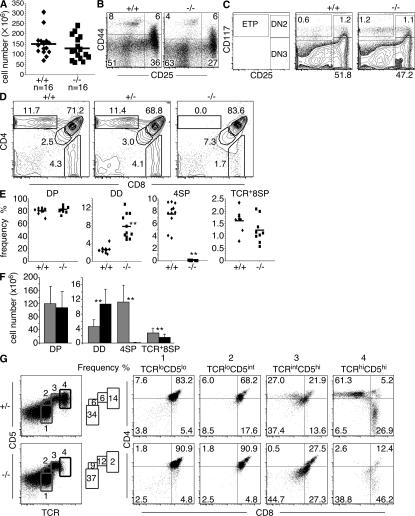
Figure 2.
TOX is required for CD4SP thymocyte development but not initiation of positive selection. (A) No statistically significant difference (P = 0.28) in total thymic cellularity of individual +/+ and −/− mice was observed. Mice ranging in age from 2.5 to 9 wk were analyzed as age-matched control and experimental pairs. Population means are shown as horizontal bars. (B) Maintenance of CD44- and CD25-defined DN subsets in lineage− (CD4−, CD8α−, B220−, DX-5−, and γδTCR−) thymocytes from Tox−/− mice. Numbers indicate frequency of DN1 (CD44+CD25), DN2 (CD44+CD25+), DN3 (CD44−CD25+), and DN4 (CD44+CD25−) subsets. (C) Maintenance of CD117- and CD25-defined DN subsets and ETP in lineage− (CD8α−, CD8β−, CD3ε−, TCR-β−, CD11b−, CD11c−, TER119−, CD19−, B220−, NK1.1−, and γδTCR−) thymocytes from Tox−/− mice. ETP (CD117+CD25−), DN2 (CD117+CD25+), DN3 (CD117−CD25+), and DN4 (CD117+CD25−) subsets are depicted. (D) Representative CD4/CD8 staining patterns of thymocytes derived from +/+, +/−, and −/− mice are shown. Numbers indicate frequency of indicated thymocyte subsets, expressed as a percentage in this figure and all subsequent figures unless otherwise indicated. (E) Compilation of the frequency of CD4- and CD8-defined thymocyte subsets in +/+ and −/− mice. CD8SP thymocytes were also gated on TCR+ cells to eliminate immature CD8SP thymocytes from the analysis. Statistically significant differences between the mean frequency of DD (P = 4.10−11) and 4SP (P = 1.10−12) +/+ and −/− thymocytes are indicated (**). (F) Absolute numbers of thymocyte subsets in +/+ (gray bars) and −/− (black bars) mice. Error bars refer to standard deviations (n = 16). Statistically significant differences between the mean absolute number of DD (P = 5.7 × 10−6), 4SP (P = 1.9 × 10−10), and 8SP (P = 0.0047) +/+ and −/− thymocytes are indicated (**) (G) Tox−/− thymocytes initiate positive selection based on marker up-regulation. Two-parameter analysis for expression of TCR-β and CD5 allows identification of developmental stages (labeled 1–4) that were then assessed for expression of CD4 and CD8.