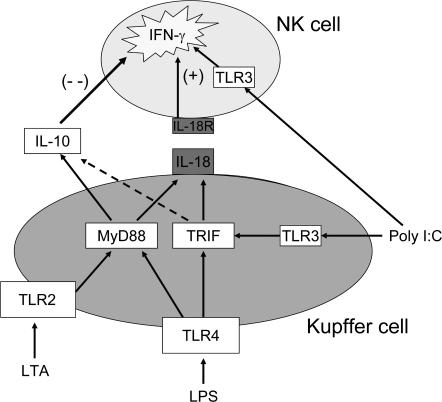
Figure 10.
Model of TLR ligand activation of Kupffer cell–NK cell cross talk in co-culture. Salient features of this model, consistent with the experimental data, are the dependence of NK activation by Kupffer cells on cell-to-cell contact, IL-18 as the critical activating signal, and IL-10 as the modulating inhibitory signal induced mainly through the MyD88 signaling cascade. The model predicts that bacteria-associated TLR agonists signaling through TLR2 and TLR4 result in down-modulated NK cell activation caused by IL-10, whereas a virus-associated TLR agonist (double-stranded RNA) acting through the MyD88-independent pathway results in stronger activation of NK cells. The model also recognizes the intracellular location of TLR3 in NK cells, as well as Kupffer cells, with the possibility of direct NK cell activation through this channel.