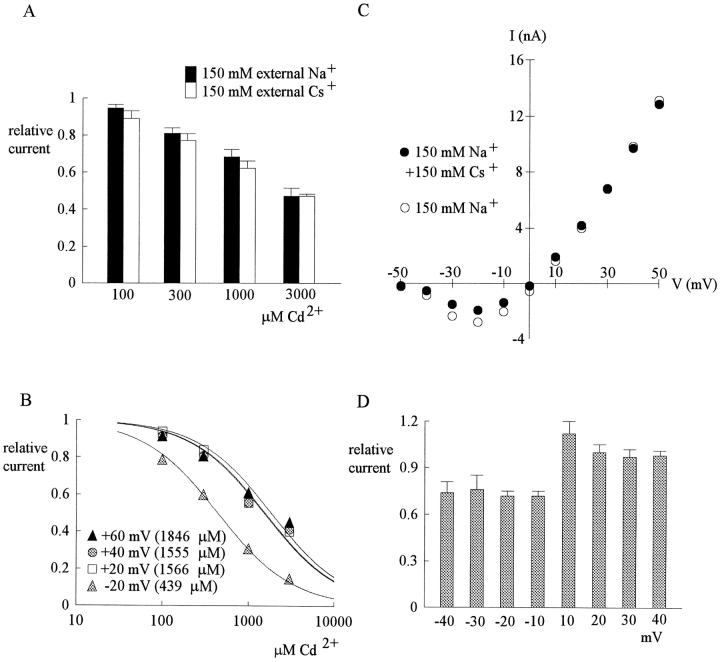
Figure 5.
The effect of external Na+ and Cs+ on Cd2+ block. (A) The relative currents in the presence of 100–3,000 μM Cd2+ at 40 mV (data from part of Figs. 1 B and 4 A) are replotted here for a better comparison. Because in either case the membrane is strongly depolarized and the internal solution contains 150 mM Na+, the Na+ current is always outward no matter the external solution contains 150 mM Cs+ (white bar, n = 4–7) or 150 mM Na+ (black bar, n = 5–7). There is no definite difference in the inhibitory effect of Cd2+ between the two cases. (B) In symmetrical 150 mM Na+ + 150 mM Cs+, the blocking effect of Cd2+ on inward (−20 mV) and outward (20–60 mV) currents is assessed in a way similar to that in Fig. 4 B. The error bars of the mean relative currents are in general <10% of the mean values and are omitted for clarity (n = 2–9). The lines are best fits for each set of data of the form: relative current = 1/{1 + ([Cd2+]/K app,Cs)}, where K app,Cs stands for the apparent dissociation constant of external Cd2+ when both outward and inward Na+ currents are elicited with symmetrical 150 mM Na+ + 150 mM Cs+ on both sides of the membrane. The K app,Cs from the fits are given in the parentheses in the figure. (C) Similar to the I-V plot in Fig. 3 B, in a dorsal root ganglion neuron the peak inward and outward Na+ currents were recorded in 150 mM external Na+ solution and in 150 mM Na+ + 150 mM Cs+ external solution, respectively, and are plotted against the test pulse voltage. Note that the inhibition of inward currents by the addition of 150 mM external Cs+ is evident, whereas the outward currents are essentially unaffected. Also note that the I-V plots are of very similar shape whether Cs+ is present or not. (D) The relative currents at each different test pulse voltages is defined as the ratio between the peak currents in the presence and absence of 150 mM Cs+ in the experiments in C (n = 4). The inhibition produced by Cs+ is similar in all inward currents (−10 to −40 mV), whereas the outward currents are clearly unaffected by Cs+.