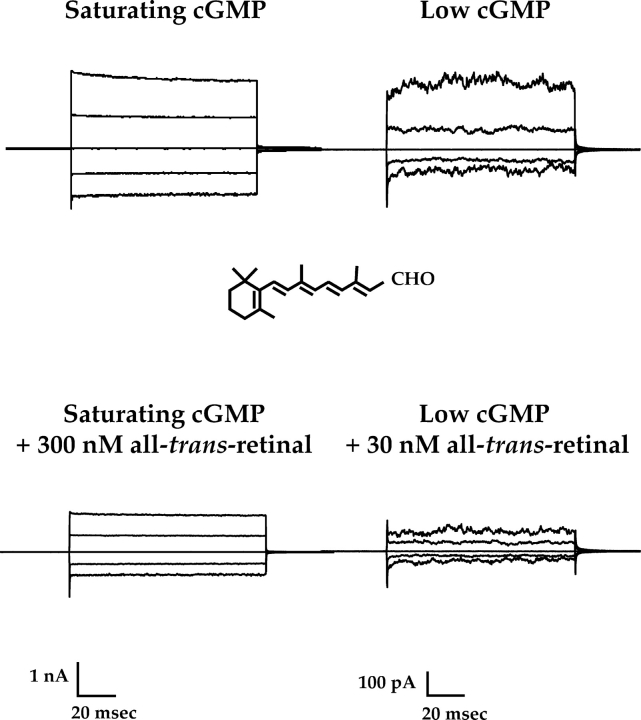
Figure 1.
ATR inhibits homomeric (CNGA1) rod channels more potently at low than at saturating cGMP concentrations. Currents were measured from multichannel, inside-out patches of homomeric (CNGA1) rod channels. The raw traces represent families of cGMP-activated currents in response to voltage steps ranging from −100 to +100 mV in 50-mV increments, from a holding potential of 0 mV. Currents measured in the absence of cGMP were subtracted from all traces. (Left) Current families depicting control and inhibition at saturating cGMP (2 mM cGMP) by 300 nM ATR (50.6% inhibition). (Right) Current families showing control and inhibition by 30 nM ATR (67.6% inhibition) at a low cGMP concentration that elicits ∼7.4% of maximal cGMP induced current.