Figure 3. Ketamine increases silver stained profiles in mouse hippocampal CA3 region.
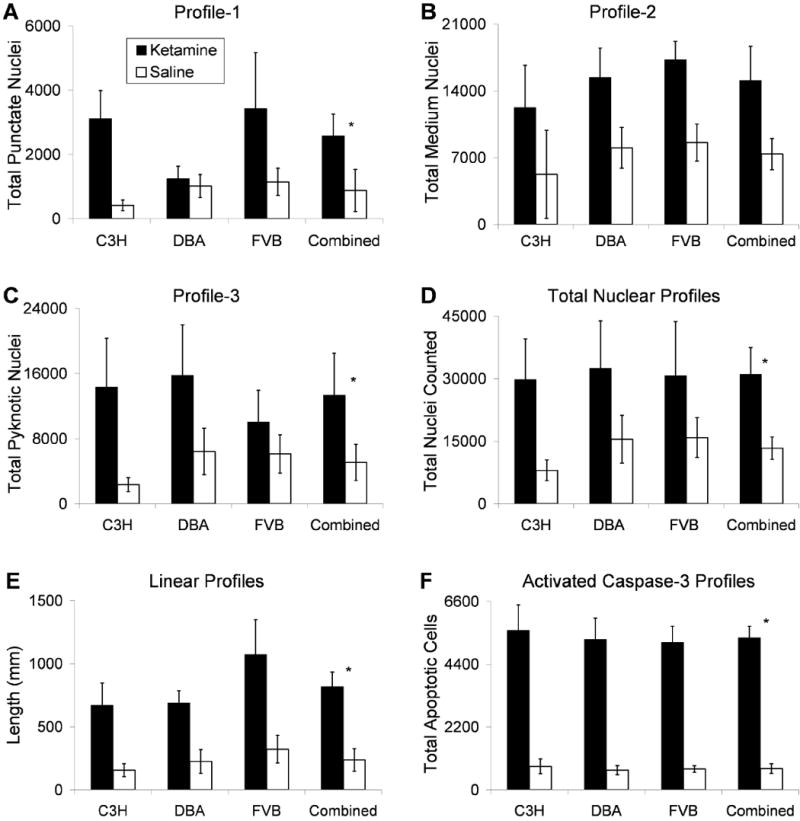
Each bar graph reflects Optical Fractionators stereological estimates for total number of specified nuclear profiles counted in murine CA3 hippocampus, weighted for empirically measured section thicknesses. Quantification was done in every fourth section (25.7μm average thickness across all mice) of C3H/HeHsd, DBA/2Hsd and FVB/Hsd mice (n = 7 or 8) that were treated 5 times with either ketamine 5 mg/kg (black bars) or normal saline (white bars) over two hours. A-C show estimates for neuronal nuclei containing: A) Profile-1, punctate labeling, diameter less than or equal to 0.8μm diameter; B) Profile-2, diameter between 0.8 and 2.5μm; C) Profile-3, pyknotic like labeling diameter greater than 2.5μm. D) The total number of degenerating nuclear profiles counted for each condition and strain are displayed. E) Length of silver labeled linear profiles. F) Population estimates of apoptotic profiles as visualized with immunocytochemistry for activated caspase-3. Analyses did not indicate a main effect of strain, therefore the final columns in each panel displays combined data of all three strains (n = 23 for ketamine, n = 23 for saline). * Note that for profile-1 (punctate), profile-3 (pyknotic), total nuclear, linear, and apoptotic profiles (A, C-E), the ANOVA revealed a main effect of ketamine treatment (p ≤ 0.02). Profile-2 (B) displayed a non-significant trend for increased labeling with ketamine (p = 0.059). Error bars depict Standard Error of the Mean for each group.
