Abstract
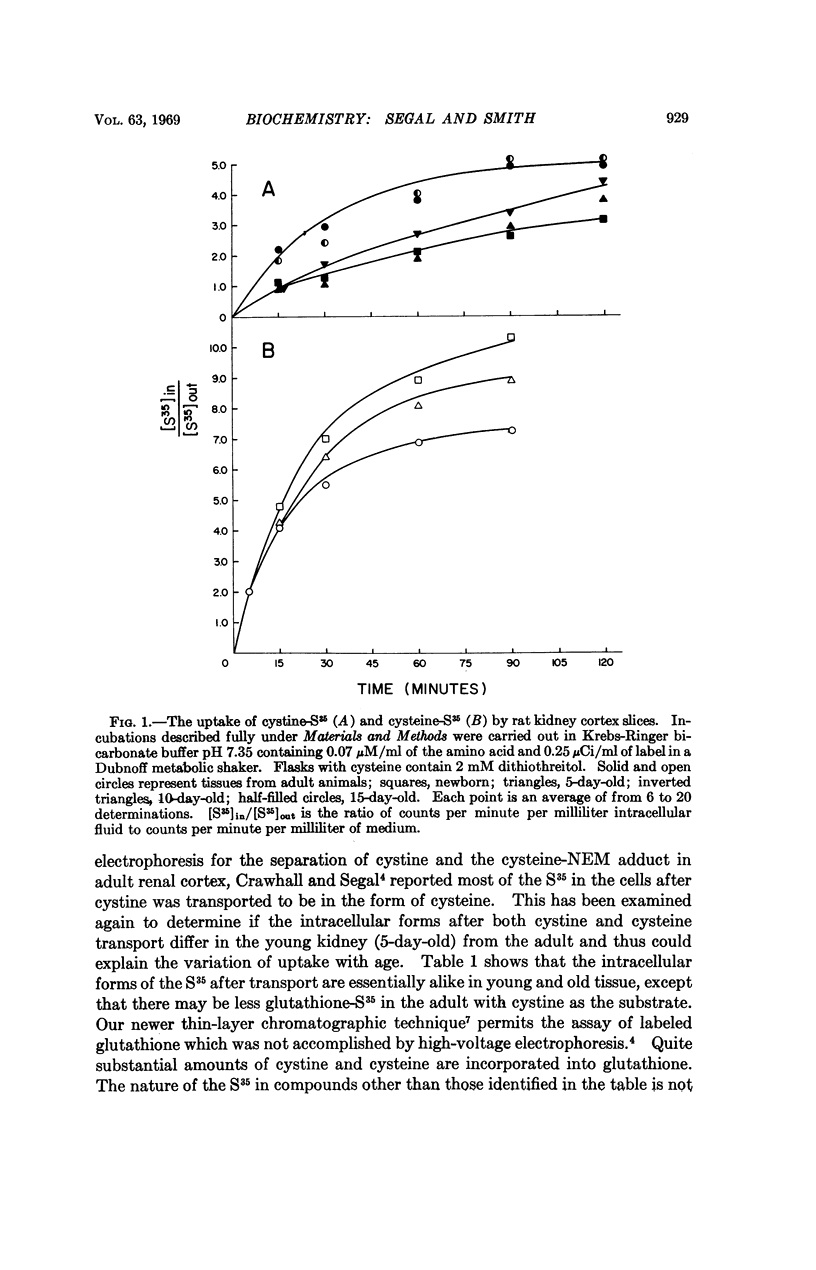
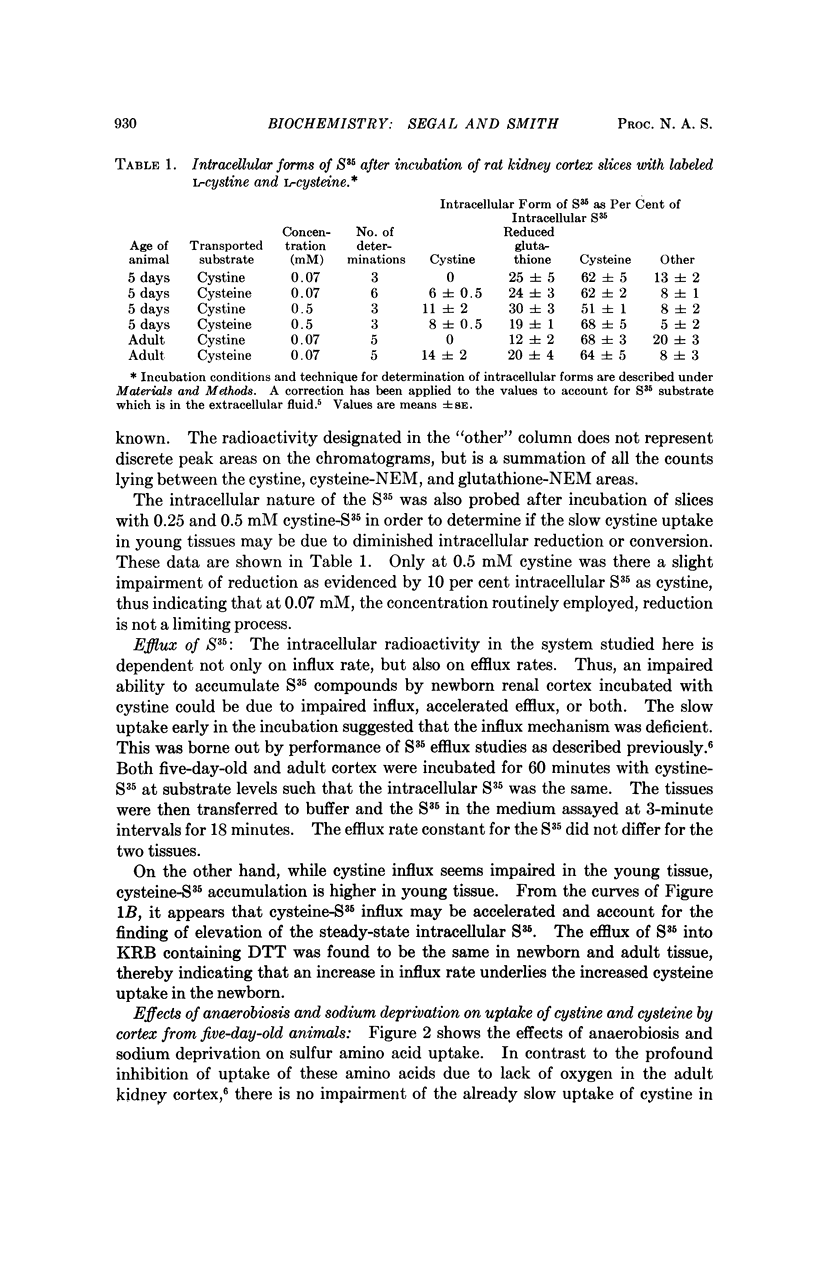
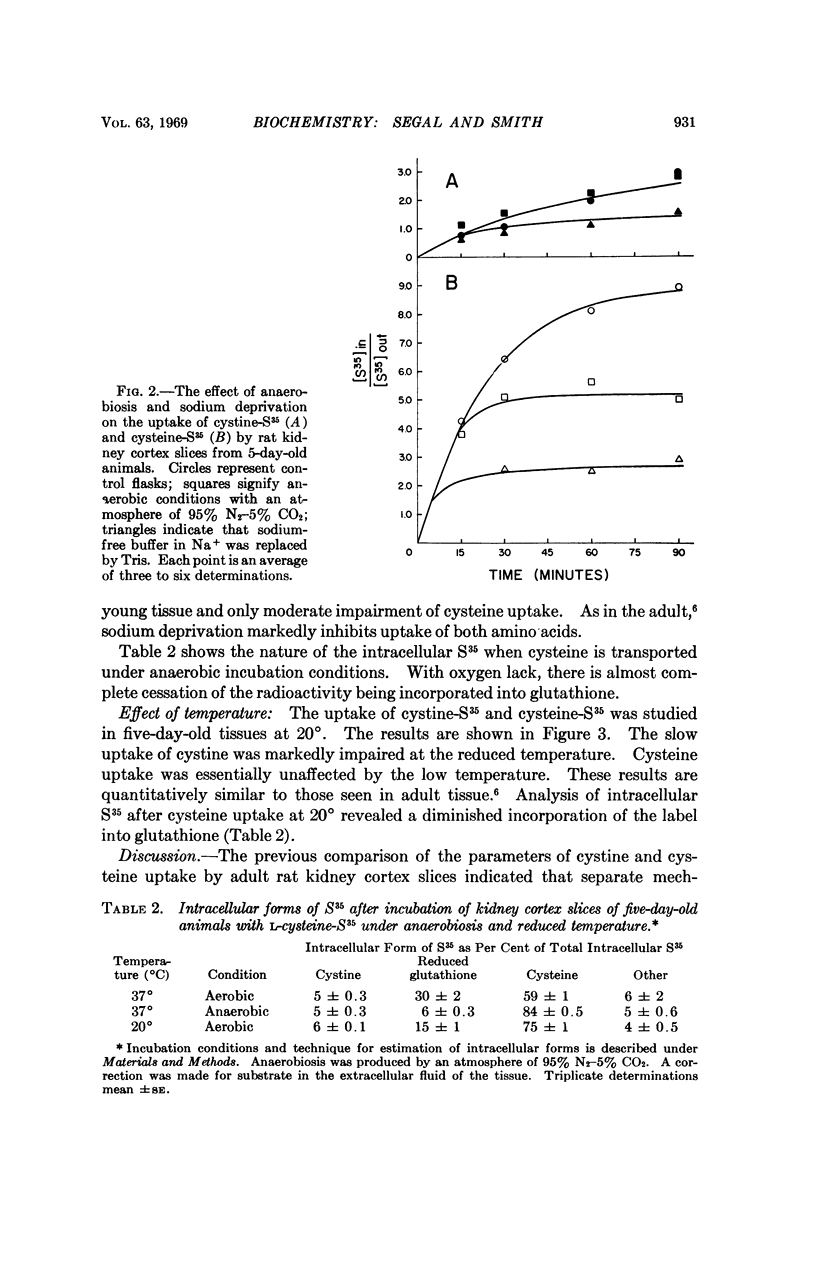
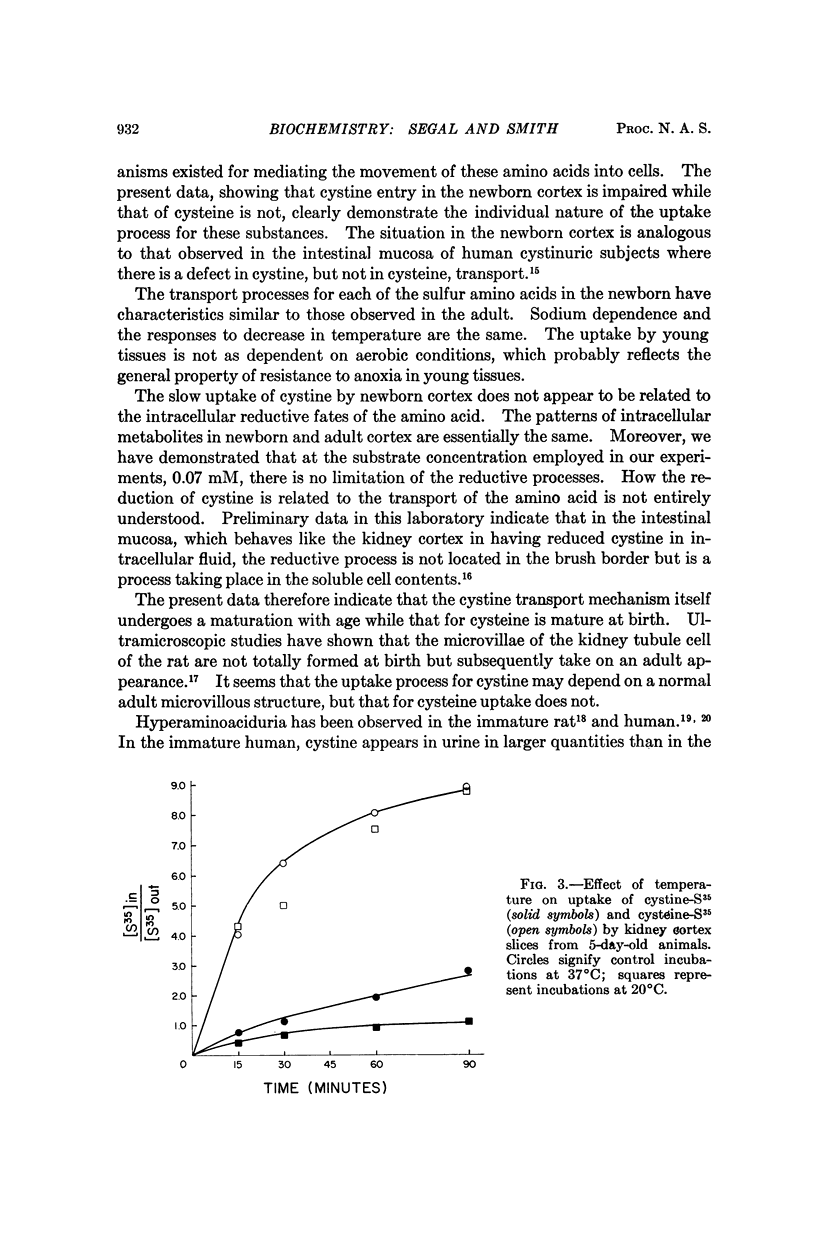
The impaired ability of neonatal rat kidney cortex slices to take up L-cystine at a time when the ability to accumulate cysteine is similar to that of adult tissues indicates the separate nature of the transport processes for these amino acids. Dissimilarities in dependence on oxygen and temperature are also indicative of different transport systems. The intracellular form of the amino acid was largely cysteine when either cystine or cysteine was the transported substrate although significant amounts of both were incorporated into reduced glutathione. No difference in intracellular forms was found between neonatal and adult tissue.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crawhall J. C., Segal S. Dithiothreitol in the study of cysteine transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 26;121(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90380-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M., THIER S., ROSENBERG L., KISER W., SEGAL S. EVIDENCE AGAINST A SINGLE RENAL TRANSPORT DEFECT IN CYSTINURIA. N Engl J Med. 1964 Mar 12;270:556–561. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196403122701105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M., THIER S., ROSENBERG L., SEGAL S. IONIC REQUIREMENTS FOR AMINO ACID TRANSPORT IN THE RAT KIDNEY CORTEX SLICE. I. INFLUENCE OF EXTRACELLULAR IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:167–176. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., BLAIR A., SEGAL S. Transport of amino acids by slices of rat-kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 23;54:479–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., DOWNING S. J., SEGAL S. Extracellular space estimation in rat kidney slices using C saccharides and phlorizin. Am J Physiol. 1962 Apr;202:800–804. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Crawhall J. C., Segal S. Intestinal transport of cystine and cysteine in man: evidence for separate mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):30–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI105508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMBAUGH R., DAVIDSON D. T., Jr, ELKINTON J. R. Variation in excretion of certain amino acids with age. Clin Chem. 1963 Apr;9:210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E., Friedmann T., Harrison H. E., Wong V., Schneider J. A. Cystinosis. Combined clinical staff conference at the National Institutes of Health. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):883–905. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Crawhall J. C. Characteristics of cystine and cysteine transport in rat kidney cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):231–237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Segal S. The influence of size of rat kidney cortex slices on the accumulation of amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):281–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States B., Segal S. Distribution of glutathione-cystine transhydrogenase activity in subcellular fractions of rat intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):443–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1130443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber W. A. Amino acid excretion patterns in developing rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;45(5):867–872. doi: 10.1139/y67-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber W. A., Cairns J. A. A comparison of the amino acid concentrating ability of the kidney cortex of newborn and mature rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;46(2):165–169. doi: 10.1139/y68-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


