Abstract
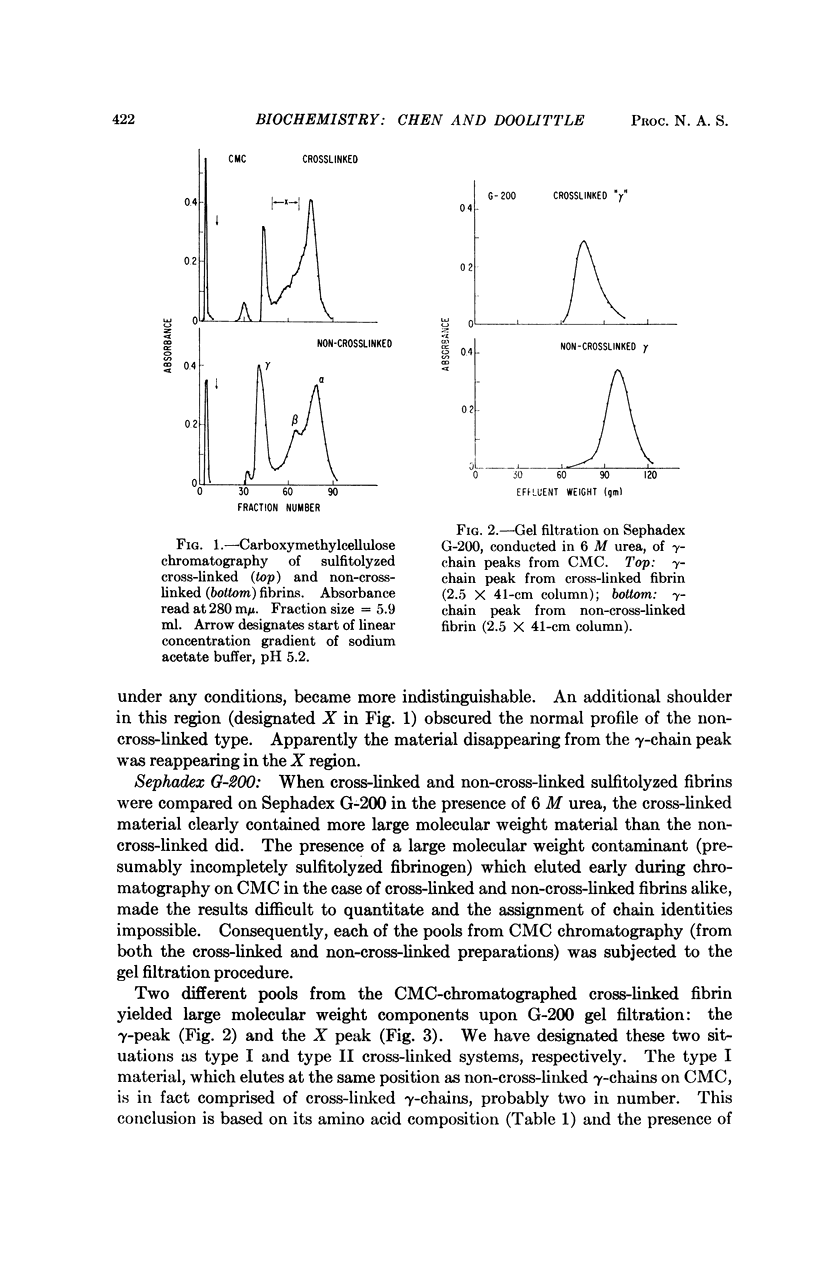
The stabilization of fibrin clots by activated factor XIII involves two different sets of cross-linked chains. In one case (type I) two γ-chains are linked to each other, indicating that γ-chains have both donor (suitable lysyl-) and acceptor (suitable glutaminyl-) functions. A second system (type II) consists of a γ-chain linked to an α-chain. Experiments with a substitute donor (glycine ethylester) indicate that only γ-chains have enzyme-accessible acceptor sites, suggesting that α-chain participation is limited to lysyl side chains. A model molecular arrangement for fibrin has been suggested which accommodates all the data.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOOLITTLE R. F. DIFFERENCES IN THE CLOTTING OF LAMPREY FIBRINOGEN BY LAMPREY AND BOVINE THROMBINS. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:735–741. doi: 10.1042/bj0940735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMAN P. Phenylthiohydantoins in protein analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Aug 31;88:602–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Cuddigan B. J. The fine structure of fibrin. Br J Haematol. 1967 May;13(3):341–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L., JACOBSEN A. SPECIFIC INHIBITORS AND THE CHEMISTRY OF FIBRIN POLYMERIZATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1939–1943. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L., KONISHI K., JACOBSEN A. Transpeptidation mechanism in blood clotting. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1148–1149. doi: 10.1038/1941148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Downey J., Gotoh T., Jacobsen A., Tokura S. The transpeptidase system which crosslinks fibrin by gamma-glutamyle-episilon-lysine bonds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 19;31(2):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L. Physiological roles of fibrinogen and fibrin. Fed Proc. 1965 Jul-Aug;24(4):784–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matacić S., Loewy A. G. The identification of isopeptide crosslinks in insoluble fibrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):356–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90750-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matacić S., Loewy A. G. Transglutaminase activity of the fibrin crosslinking enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):858–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Rogers L. A., Marler E., Hill R. L. The subunit polypeptides of human fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHERE J. F., DIXON G. H., MAYBURY R. H., NEURATH H. Cleavage of disulfide bonds in trypsinogen and alpha-chymotrypsinogen. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1364–1372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P. [Cross-link in fibrin polymerized by factor 13: epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine]. Science. 1968 May 24;160(3830):892–893. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3830.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Page I. H., Shainoff J. R. Stable complex of fibrinogen and fibrin. Science. 1966 May 20;152(3725):1069–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3725.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


