Figure 1.
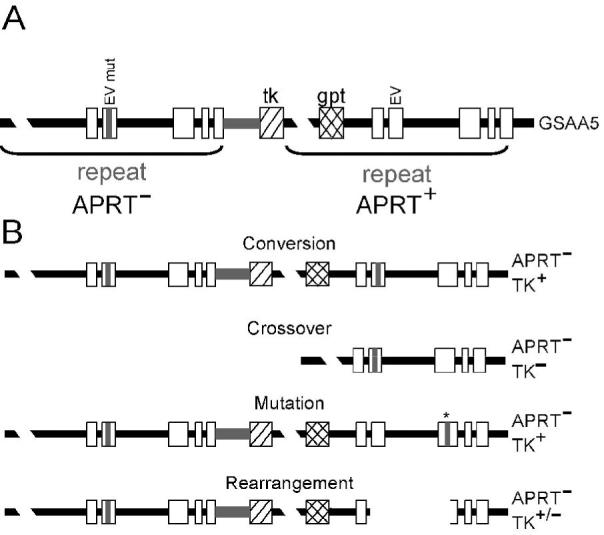
Recombination substrate and products. A. The duplication at the Aprt locus in GSAA5 cells. The upstream copy of Aprt contains a mutated EcoRV site (EV mut) in exon 2, as well as a truncated exon 5, rendering it nonfunctional. The downstream copy contains the normal EcoRV site (EV) and is functional, making GSAA5 cells APRT+. The herpes virus thymidine kinase (TK) and the guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (gpt) genes served as additional selective markers useful in generating the GSAA5 cell line and for characterizing the recombination products. B. Illustrations of the types of APRT- colonies that arise in GSAA5 cells. After selection against APRT function, it is possible to recover clones that underwent HR (conversions or crossovers), mutation of the wild-type copy of the Aprt gene (indicated by the * above exon 3), or rearrangement of the Aprt gene (shown here as a deletion of a portion of the Aprt gene). Each of these events can be distinguished by a combination of Southern blot and PCR analysis (see Materials and Methods).
