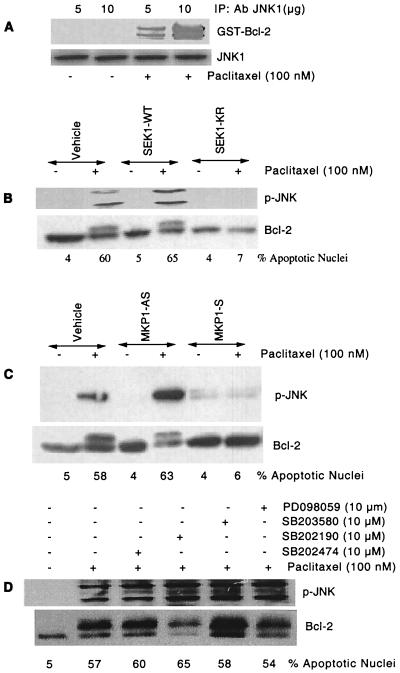
Figure 2.
Block of JNK pathway inhibits paclitaxel-induced Bcl-2 phosphorylation and apoptosis. (A) JNK phosphorylates GST-Bcl-2 in vitro (Upper). MCF-7 cells were treated with paclitaxel (100 nM) for 4 h, and activated JNK1 was immunoprecipitated with either 5 μg or 10 μg anti-JNK1 antibody. GST-Bcl-2 (10 μg) was incubated with immunoprecipitated JNK1 in vitro (see Materials and Methods). The same blot was reprobed with anti-JNK1 antibody (Lower). (B) A dominant-negative mutant SEK1 (K→R) inhibits activation of the JNK pathway, Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and apoptosis induced by paclitaxel (100 nM). MCF-7 cells were transfected with a total of 2 μg/ml DNA of either empty vector (−) or mutated SEK1 (+) and incubated for 1 day. Cells were washed and incubated with fresh medium. After 8 h, the cells were incubated with 100 nM paclitaxel (+) or vehicle (−) for 30 min, 4 h, and 24 h for the measurement of JNK activation, Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and apoptosis, respectively. The JNK activity and immunoblottings were determined as described. (C) Effect of MKP-1 on JNK activation and Bcl-2 phosphorylation. MCF-7 cells were transfected with 30 μg anti-MKP-1 antisense (MKP-1-AS) or sense vector (MKP1-S) with Lipofectamine and incubated for 1 day. Cells were washed, and fresh medium was replaced. After 8 h, the cells were incubated with 100 nM paclitaxel (+) or vehicle (−) for 30 min, 4 h, and 24 h for the measurement of JNK activation, Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and apoptosis, respectively. (D) Effect of ERK and p38 inhibitors on JNK activation and Bcl-2 phosphorylation. MCF-7 cells were pretreated with inhibitors of ERK (PD098059), p38 (SB203580, SB202190), or negative control (SB202474) for 1 h. They were exposed to paclitaxel for 30 min, 4 h, and 24 h to determine JNK activation, Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and apoptosis, respectively.