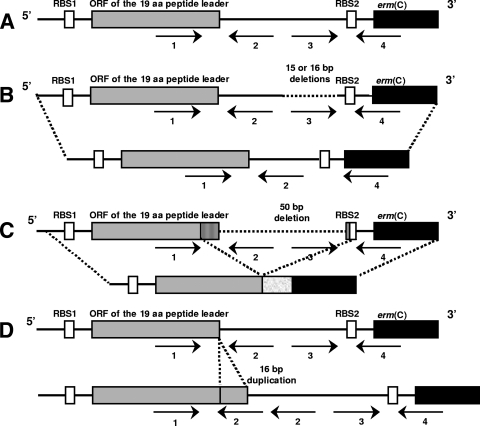
FIG. 2.
Schematic presentation of the regulatory regions of the inducibly expressed erm(C) gene from S. aureus 9 (A) and the constitutively expressed erm(C) genes selected in this study (B, C, and D). RBS1 and RBS2, ribosome binding sites of the leader peptide and the erm(C) gene, respectively. Arrows indicate the inverted repeated sequences IR1 to IR4. (A) Wild-type erm(C) gene; (B) derivatives with 15- and 16-bp deletions in IR3; (C) derivative with a 50-bp deletion (deletion of the stop codon of the leader peptide generates a translational fusion with the methylase); (D) derivative with tandem duplication of a 16-bp sequence (insertion of a new IR2).