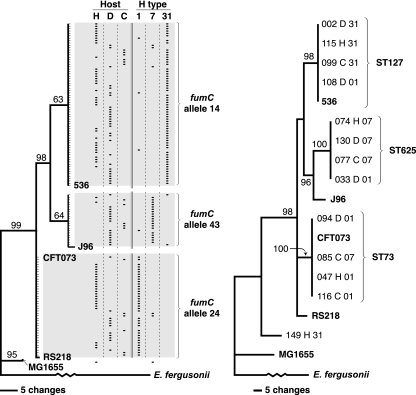
FIG. 1.
Phylogeny of 130 Escherichia coli isolates of serogroup O6 from humans, dogs, and cats according to fumC (left) (total population) or adk, fumC, gyrB, icd, mdh, purA, and recA (right) (representatives of each fumC allele). Trees were inferred using maximum parsimony. Bootstrap values of >60% (from 1,000 iterations) are shown. In the fumC tree (left), fine tick marks indicate individual study isolates with identical sequences. In the composite tree (right), each study isolate's unique identification number and (7-locus) sequence type (ST) are given. In both trees, study isolates are labeled with the host species (H, human; D, dog; C, cat) and H type (1, 7, or 31). According to the Achtman scheme, fumC alleles 14 (91% H31), 24 (92% H1), and 43 (82% H7) correspond to STs 127, 73, and 625, respectively. Reference strains 536, J96, CFT073, RS218, and MG1655 are included for comparison.