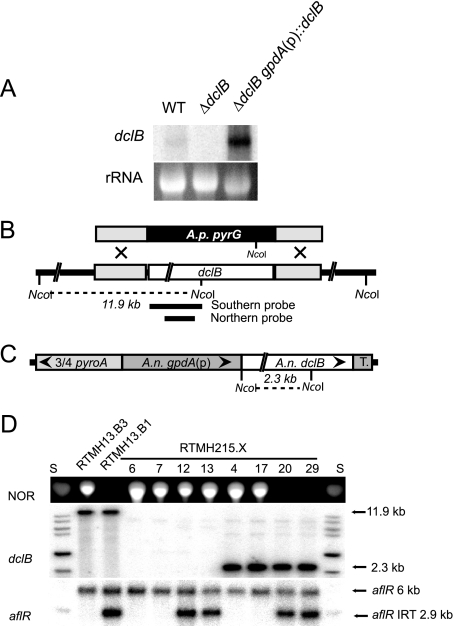
FIG. 7.
A. nidulans dclB is required for IRT-RNA silencing. (A) Northern blotting identifies dclB transcript in total RNA from 48-h cultures. The ethidium bromide-stained 26S rRNA band is shown. Strains: WT, RTMH13.B3; ΔdclB, RTMH215.6; ΔdclB gpdA(p)::dclB, RTMH215.4. (B) Schematic representation of dclB replacement with pyrG. Gray boxes represent the dclB flanking sequences used in the deletion vector. The white box represents the predicted A. nidulans dclB ORF. (C) Schematic representation of dclB complementation by targeting a gpdA::dclB construct to the pyroA locus. (D) NOR analysis and Southern blotting (HindIII digest for dclB, NcoI-HindIII digests for aflR) results for control strains and recombinants from a cross between a ΔdclB transformant (TTMH158.1) and a transformant carrying the gpdA(p)::dclB transgene (TTMH160.3). Note that the absence of a band for dclB indicates the deletion genotype (see the probe template in panel B) and that the presence of two bands for aflR indicates the IRT genotype. Because normal levels of NOR are detected for the ΔdclB aflR(IRT) genotype, the data indicate that RNA silencing is dependent on dclB. S, NOR standard or 1-kb ladder.