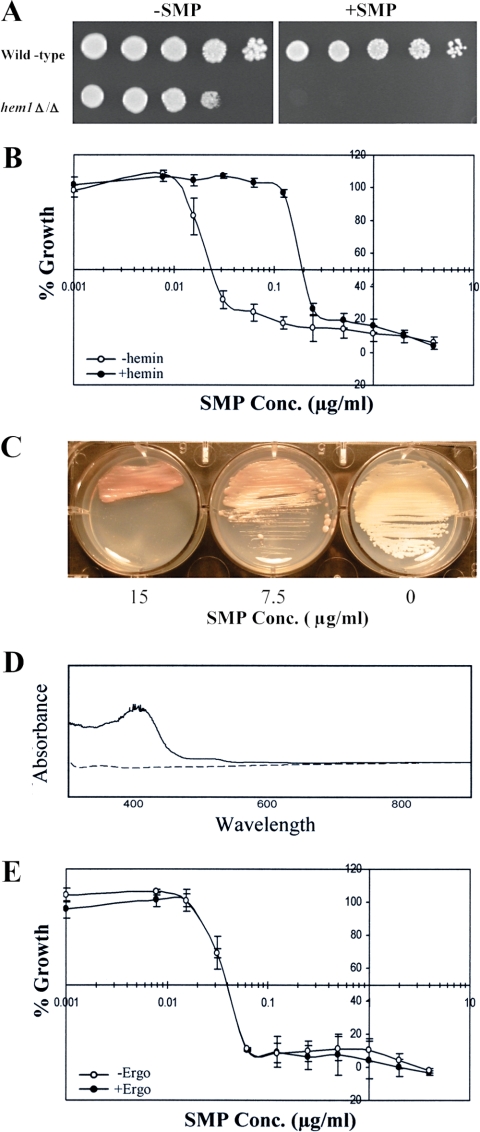
FIG. 7.
Role of heme in the activity of sampangine in C. albicans. (A) Dilutions (fivefold) of wild-type (BWP17) and hem1Δ/Δ (KRC1) strains grown as described in Materials and Methods were inoculated onto YPD + Uri + ALA (8 μg/ml) agar medium and incubated for 2 days at 30°C. −SMP, medium containing solvent (DMSO); +SMP, medium containing sampangine at 5 μg/ml. (B) Results shown are from broth microdilution assays performed in triplicate on C. albicans strain SC5314 in the presence of various concentrations (Conc.) of sampangine with 32.5 μg/ml hemin (+hemin) or without hemin (−hemin). Percent growth is shown as the mean ± SEM. (C) C. albicans strain SC5314 colonies grown on YPD agar were streaked on SD agar medium containing various concentrations (Conc.) of sampangine and incubated for 3 days at 30°C. The 0 represents medium containing solvent (DMSO). (D) Absorption spectra of alkaline pyridine extracts prepared from C. albicans strain SC5314 cells treated with sampangine (solid line) or with DMSO solvent (dashed line). (E) Results are shown from broth microdilution assays performed in triplicate on C. albicans strain SC5314 in the presence of various concentrations (Conc.) of sampangine with 10 μg/ml ergosterol (+Ergo) or without ergosterol (−Ergo). Percent growth is shown as the mean ± SEM.