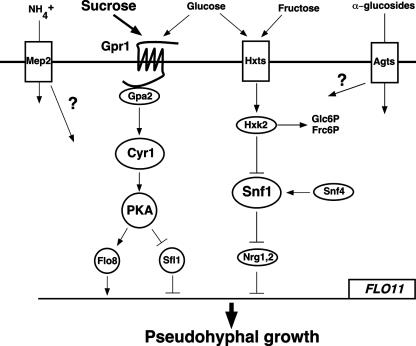
FIG. 4.
Simplified scheme depicting the sensing and signaling components involved in the induction of pseudohyphal growth by hexose (glucose and fructose) and alpha-glucoside sugars (sucrose, maltose, and maltotriose). Glucose and sucrose activate PKA through Gpr1, Gpa2, and adenylate cyclase (Cyr1), leading to the induction of FLO11 transcription by controlling the activities of transcription regulators, such as Flo8 and Sfl1. Monomeric hexose sugars inhibit pseudohyphal growth by inactivating the Snf1 kinase upon uptake by hexose transporters (Hxts) and phosphorylation by hexokinase 2 (Hxk2). Snf1 is known to induce filamentation by inactivating the repressor proteins Nrg1 and Nrg2 and is itself activated by its γ subunit, Snf4. Maltotriose and possibly other alpha-glucoside sugars activate pseudohyphal growth upon or after transport across the plasma membrane by alpha-glucoside transporters (Agts). The ammonium permease Mep2 is required for pseudohyphal growth in the presence of ammonium, but how it links to the other pathways is unclear.