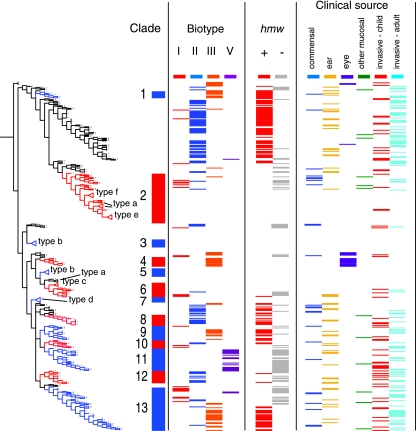
FIG. 2.
Characterization of NTHI strains and correlation of biotype and hmw locus with clustering on the majority-rule consensus tree. The tree differs from that in Fig. 1 in that each ST found in more than one NTHI strain was expanded to allow plotting of data for each strain, while serotype-specific clusters were collapsed (indicated by triangles). The tree is aligned with a plot showing clade (as in Fig. 1), biotype, the presence of the hmw loci (determined by PCR), and the type of specimen from which the strain was cultured. Commensal, strains cultured from oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal swabs from healthy children; otitis, strains from middle ear aspirates from children with otitis media; eye, strains from children with conjunctivitis; mucosal, strains from other mucosal samples, primarily sputum or endotracheal aspirates; invasive, strains from blood or cerebrospinal fluid. The biotype and PCR data, including the results of PCR of the LPS biosynthetic locus flanked by infA and ksgA, are summarized in Table 1.