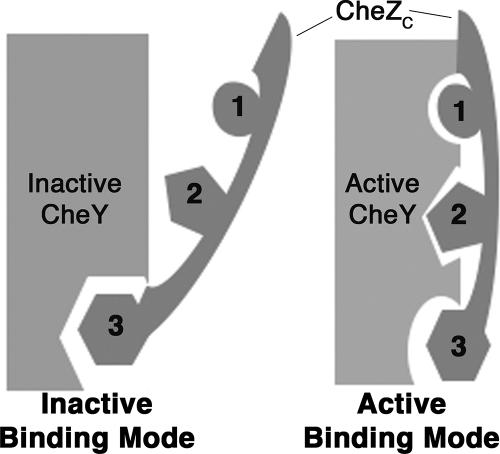
FIG. 1.
Schematic illustration of the state-specific dual-binding model. Discrete modes of CheZC peptide binding to CheY are correlated with different conformational states of CheY, i.e., inactive binding mode for binding to inactive CheY and active binding mode for binding to activated CheY. The CheZC peptide binds to the α4-β5-α5 surface of CheY in both modes. In the inactive mode, the majority of the interactions are through C-terminal Phe214 (residue no. 3; depicted as hexagons) and the N terminus is exposed to the solvent; in the active mode, the surface buried by C-terminal Phe214 is reduced while electrostatic contacts involving N-terminal residues Gln202 (residue no. 1; depicted as circles) and Asp206 (residue no. 2; depicted as pentagons) are responsible for burying the N terminus of the CheZC peptide to the α4-β5-α5 face of CheY. In the absence of CheY activation, when the CheZC peptide is bound in the inactive mode, CheY is in a meta-active state (13).