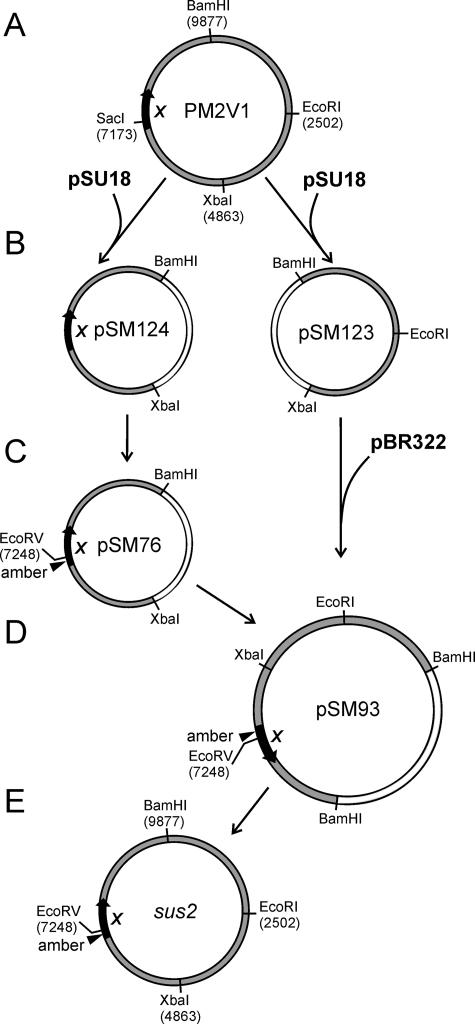
FIG. 3.
Genetic engineering of the PM2 genome to construct the sus2 amber mutant. (A) Four unique restriction enzyme cleavage sites were introduced into the PM2 genome, resulting in PM2V1. The position of gene X is indicated. (B) PM2V1 was digested with BamHI and XbaI, and the two fragments were cloned into the corresponding sites of the pSU18 vector, generating plasmids pSM123 and pSM124. (C) pSM124 was used as a template to introduce a nonsense mutation in gene X (substituting a His47 codon for a TAG codon) and an EcoRV restriction cleavage site for screening, resulting in plasmid pSM76. (D) PM2-specific fragments were BamHI-XbaI double digested from the plasmids pSM123 and pSM76 and ligated with BamHI-digested pBR322 vector, generating plasmid pSM93. (E) The mutated genome amplified in E. coli was cut out with BamHI from pSM93 and ligated into circular form, resulting in the PM2 sus2 mutant. See the text and Table 1 for details. The numbers refer to the PM2 genome coordinates (GenBank accession no. AF155037).