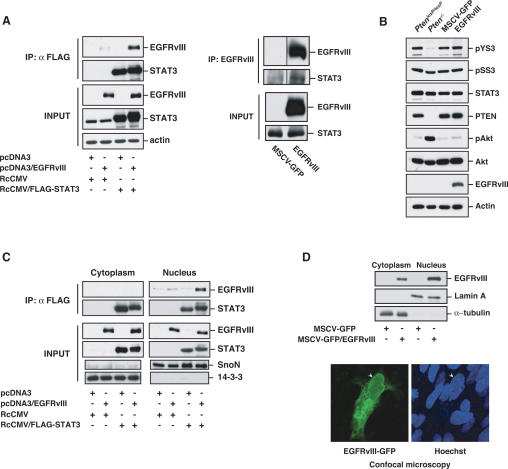
Figure 4.
STAT3 interacts with EGFRvIII in the nucleus. (A, left panel) Lysates of 293T cells transfected with expression plasmids encoding Flag-STAT3, EGFRvIII, or both were immunprecipitated with a Flag antibody followed by immunoblotting with an EGFR or STAT3 antibody. Total lysates (Input) were also immunoblotted with these antibodies. Actin served as loading control. EGFRvIII interacted efficiently with STAT3. (Right panel) Lysates of stable MSCV-GFP and MSCV-GFP/EGFRvIII astrocytes were immunoprecipitated with an EGFRvIII antibody followed by immunoblotting with an EGFR or STAT3 antibody. Total lysates (Input) were also immunoblotted with these antibodies. EGFRvIII interacted with endogenous STAT3 in astrocytes. (B) Immunoblotting of PtenloxP/loxP and Pten−/− astrocytes, or stable MSCV-GFP and MSCV-GFP/EGFRvIII astrocytes with antibodies that recognize Tyr705-phosphorylated STAT3 (pYS3), Ser727-phosphorylated STAT3 (pSS3), total STAT3, PTEN, Ser473-phosphorylated Akt (pAkt), total Akt, and EGFR. Actin was used as loading control. EGFRvIII expression had little effect on STAT3 Tyr705 and Ser727 phosphorylation. (C) Lysates of 293T cells transfected with Flag-STAT3, EGFRvIII, or both were fractionated into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions and then subjected to immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses as in A. SnoN and 14–3–3 were used as nuclear or cytosolic markers, respectively. EGFRvIII interacted with STAT3 more efficiently in the nuclear than in the cytoplasmic fraction. (D) EGFRvIII is present in the nucleus of astrocytes. (Top panel) Lysates of EGFRvIII-expressing and control astrocytes were subjected to subcellular fractionation and immunoblotting with the EGFR antibody. Lamin A and α-tubulin were used as nuclear or cytosolic markers, respectively. (Bottom panel) Immortalized astrocytes transfected with a plasmid encoding an EGFRvIII-GFP fusion protein were fixed and imaged by confocal microscopy to detect GFP fluorescence. Hoechst was used to visualize nuclei. Arrowheads indicate the position of the nucleus.