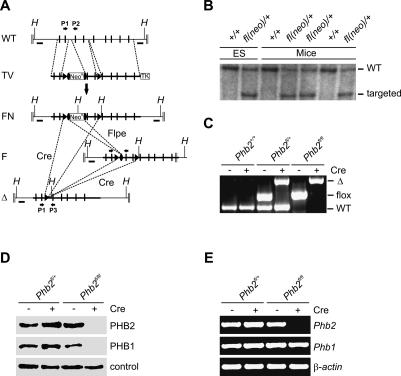
Figure 1.
Conditional inactivation of murine Phb2 in vivo and in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the wild-type Phb2 locus (WT), the targeting vector (TV), the targeted Phb2fl(neo)/+ locus after homologous recombination (FN), the conditional Phb2fl/fl locus after Flpe-mediated recombination (F), and the knockout locus upon Cre-mediated recombination (Δ). Positive and negative selection markers (NeoR and TK), exons (black bars), FRT and loxP sites (black ovals and black triangles, respectively), external probes (black boxes, A and B), locations of PCR primers (black arrows, P1–P3), and relevant HindIII restriction sites (H) are indicated. (B) Southern blot analysis of germline transmitted offspring harboring the targeted Phb2fl(neo)/+ locus. Genomic DNA isolated from ES cells and tail biopsies was digested with HindIII, hybridized, and analyzed by autoradiography. (C) PCR analysis of DNA isolated from MEFs. Amplified DNA fragments for the wild-type (WT), floxed (flox), and knockout (Δ) locus are shown. (D) Immunoblot analysis of total protein lysates. MEFs, transduced with Cre-recombinase when indicated, were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting using PHB1- and PHB2-specific antibodies. A cross-reacting band was used as a loading control. (E) RT–PCR analysis of Phb1 and Phb2 transcripts in Phb2-deficient and control MEFs. Transcripts of β-actin were used as control.