Figure 1.
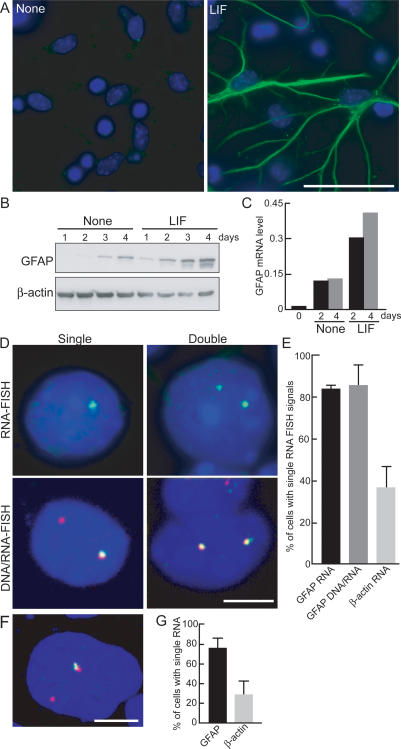
Monoallelic expression of GFAP. NPC prepared from E14 mice were treated with LIF for 4 d and stained with anti-GFAP antibody (green, GFAP; blue, DAPI) (A) and GFAP protein detected by Western blotting (B). (C) RT–PCR analysis of GFAP mRNA. mRNA was prepared from NPC incubated with or without LIF for 2 or 4 d and subjected to real-time quantitative PCR. GFAP mRNA levels were normalized to β-actin mRNA expression. (D) Monoallelic expression of GFAP. RNA FISH (top panels) or simultaneous DNA/RNA FISH (bottom panels) was performed in NPC treated with LIF. (Green) GFAP RNA; (red) GFAP DNA. (E) Quantitation of monoallelic expression of GFAP. The percentage of cells with a single RNA FISH signal is indicated. Values are averages from two to three experiments ± SEM. N = 41–127. (F) Expression of GFAP in astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were taken from neonatal mice cerebral cortex, and after two passages, simultaneous DNA/RNA FISH for GFAP was performed. (Red) GFAP DNA; (green) GFAP RNA. (G) Quantitation of active GFAP alleles in primary astrocytes. The percentage of cells with a single RNA FISH signal is indicated. Values are averages from three experiments ± SEM. N = 36–248. Bars: A, 50 μm; D,F, 5 μm.