Fig. 6. Model of the organization of cohesin and pericentric chromatin in metaphase.
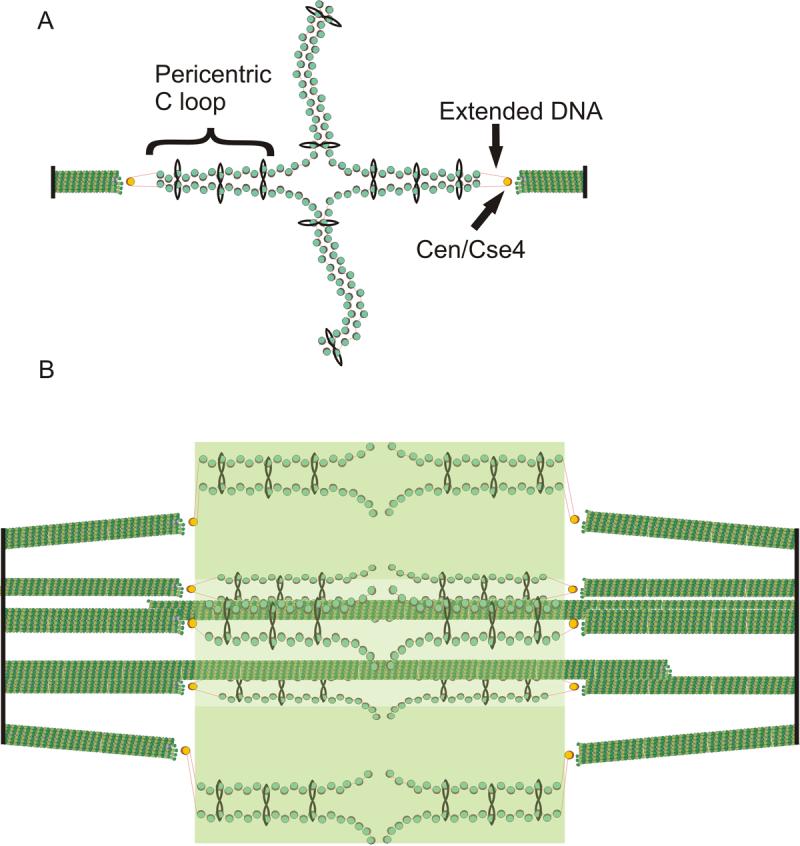
(A) DNA of each sister chromatid is held together via intramolecular bridges that extend approximately 11.5kb on either side of the centromere. There is a transition from intra- to intermolecular linkages resulting in a cruciform structure. (B) 5 (of 16) bioriented sister chromatids are shown with two (of 8) interpolar microtubules. We have proposed that the transition between intramolecular looping and intermolecular cohesion is mobile and on average 7kb from the centromere core [18]. DNA adjacent to the centromere may extend to its B-form length in vivo (as described in text, depicted as red lines) linking the centromere at kinetochore microtubule plus-ends to strands of intramolecularly paired pericentric chromatin and cohesin that are displaced radially from spindle microtubules. Microtubules (green rods), spindle pole bodies (black rods), 125 bp centromere (wrapped around the Cse4-containing histone in yellow), nucleosomal chromatin (green histone cores wrapped around DNA in red), cohesin (black circles). The fluorescence distribution of cohesin is depicted in transparent green. Pericentric chromatin from each of the 16 chromosomes is displaced 70−90nm radially from the central spindle microtubules. The entire spindle is composed of 32 kinetochore microtubules and 8 pole-pole microtubules.
