Figure 2. Monarch-1 suppresses both canonical and noncanonical NF-κB activation.
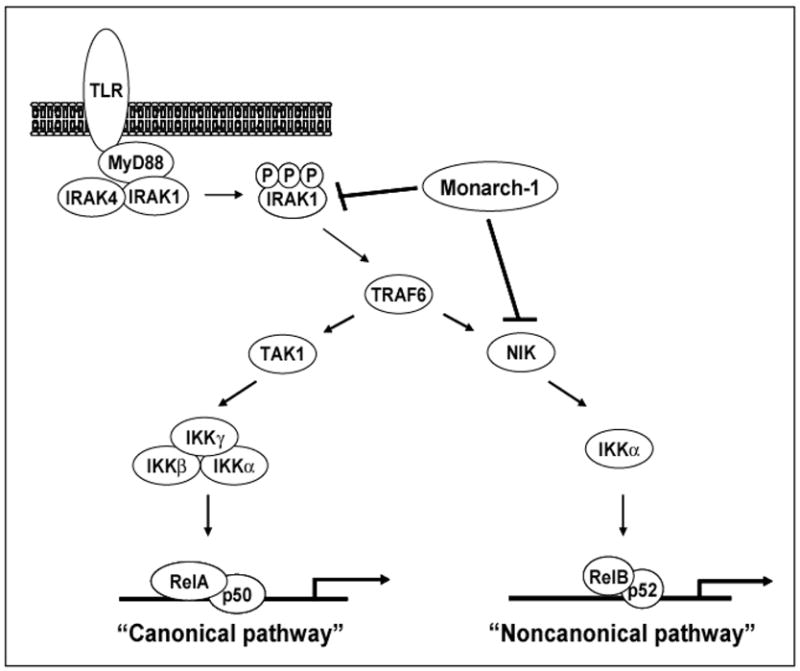
Upon TLR stimulation, the adaptor protein MyD88 is recruited to the receptor complex. MyD88 then recruits IRAK4 and IRAK1 which results in the accumulation of hyperphosphorylated IRAK1. This leads to the activation of TRAF6 which triggers NF-κB activation via MAP3 kinases such as TAK1 and NIK. While the canonical pathway can be activated by a number of upstream kinases, the noncanonical pathway is strictly dependent upon NIK. Monarch-1 is capable of blocking both pathways through its interactions with IRAK1 and NIK. Monarch-1 suppresses canonical NF-κB activation by blocking the accumulation of hyperphosphorylated IRAK1. The noncanonical pathway is also inhibited as the association of Monarch-1 with NIK leads to rapid proteasome dependent degradation of the kinase.
