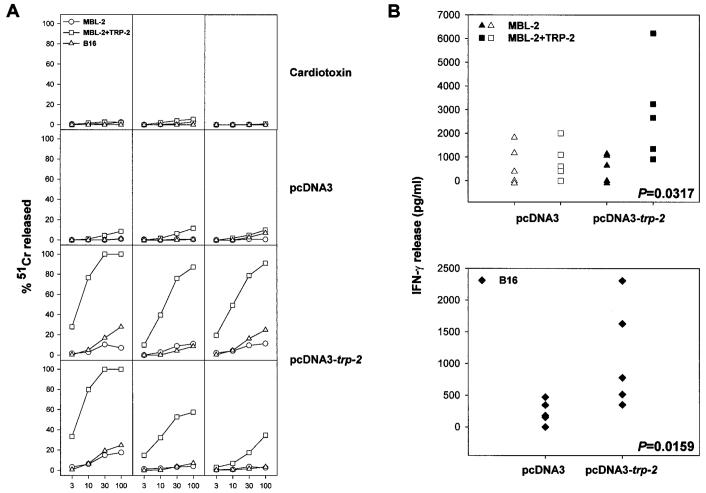
Fig. 1.
Plasmid DNA encoding TRP-2 induces Ag-specific CTL. A, 3 weeks after i.m. inoculation of plasmid DNA, spleens were removed, and splenocytes were stimulated in vitro in an MLPC with 1 μm of TRP-2180–188 peptide. After 5 days of culture, cytotoxic activity of the splenocytes was tested in a 51Cr release assay carried out for 5 h against the following target cells: MBL-2, MBL-2 pulsed with TRP-2180–188 peptide, and B16. Each panel shows the CTL response generated in a single mouse after inoculation of either cardiotoxin alone or cardiotoxin followed by either the empty pcDNA3 vector or pcDNA3-trp-2. Results are representative of five experiments. The SD of the triplicate determinations for each effector/target cell ratio (E:T ratio) was <10%, and spontaneous release never exceeded 20%. B, splenocytes (105 cells) from MLPCs were restimulated for 24 h in triplicate wells with an equal amount of MBL-2 cells, MBL-2 cells pulsed for 1 h with 1 μm TRP-2180–188 peptide, or B16 melanoma cells; the supernatant was then harvested and tested for released IFN-γ in a sandwich ELISA assay. The SD of the triplicate determinations for each effector/stimulator combination was <10%, and IFN-γ measured in control wells containing either effectors or stimulators alone did not exceed the lowest amount of IFN-γ detectable in our assay (i.e., 547 pg/ml, determined using serial dilutions of IFN-γ). Two-tailed Ps calculated by the Mann-Whitney test are reported in the figure for those groups showing significant differences over their respective controls (filled symbols).