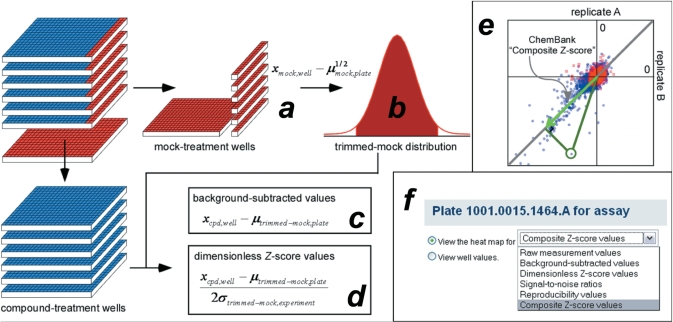
Figure 4.
ChemBank standard data-analysis model for high-throughput small-molecule screens. All raw small-molecule assay results in ChemBank are further processed by comparing each measurement with the collection of mock-treatment well measurements performed in the same screening experiment. Median values from mock-treatment wells on the same plate are used in an initial zero-centering step (a), after which the distribution of mock-treatment measurements for the entire experiment is trimmed to eliminate systematic artifacts (b). Trimmed mock-treatment measurements are used to normalize assay performance by first subtracting the mean of trimmed mock-treatment measurements on the same plate to give ‘background-subtracted values’ (c), then dividing by twice the standard deviation of trimmed mock-treatment measurements for the entire experiment to give ‘dimensionless Z-score values’ (d). Replicate handling is performed by cosine correlation of the replicate pair (for screens done in duplicate) of ‘dimensionless Z-score values’ for each compound with a simple prior model of ‘perfect reproducibility’, to yield a ‘Composite Z-score value’ (e) that represents the final primary screening result. The ChemBank web interface provides access to raw and processed data types appropriate for each of its visualization tools (f).