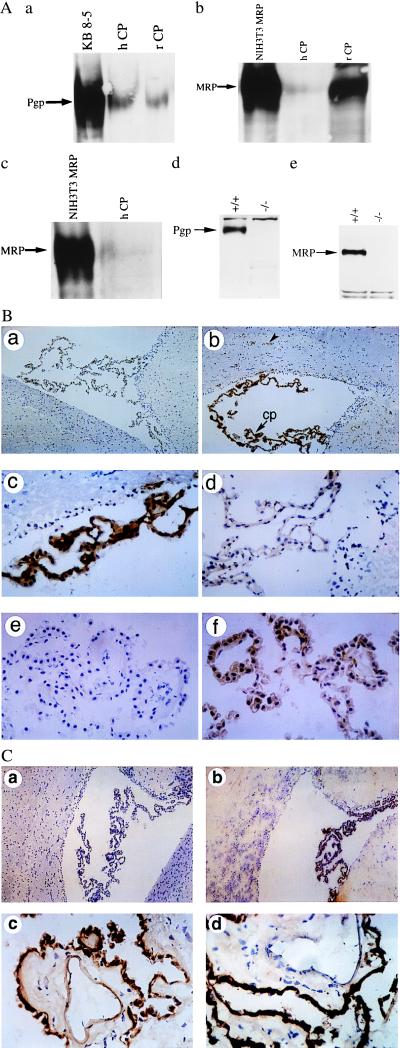
Figure 2.
(A) Expression of Pgp and MRP (arrows) in enriched membrane fractions of CP from rat (rCP) and human (hCP) shown by immunoblotting with C219 (a), MRPr1 (b), and QCRL-1 (c). Disruption of Pgp and MRP expression in cell lysates of CP isolated from FVB mdr1a/1b(−/−) and C57Bl/6 mrp(−/−) gene knockout mice, respectively, compared with their wild-type littermates shown by immunoblotting with C219 (d) and MRPr1 (e). C219 detects a protein of 170 kDa that comigrates with MDR1 Pgp expressed in human multidrug-resistant KB 8-5 cells, whereas MRPr1 and QCRL-1 detect a protein of 190 kDa that comigrates with recombinant human MRP expressed in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. In all lanes 50 μg of protein was used, except for NIH 3T3 MRP (25 μg). (B) Localization of Pgp to epithelial cells of rat and human CP by immunohistochemistry. Frozen rat brain tissue is stained in the absence of primary mAb (a; ×100), with mAb C219 (b; ×100), or with C219 (c; ×400); staining is abolished competitively by preequilibrating C219 in a 1,000-fold molar excess of a synthetic epitope-specific blocking peptide (d; VVQEALDKAREGRTC; ×400). Frozen human CP is stained in the absence of primary mAb (e; ×400) and in the presence of mAb MRK16 (f; ×400). Human CP epithelial cell-specific expression also was confirmed by peptide-displaceable staining with C219 (data not shown). (b) cp, CP within a lateral ventricle; the arrowhead indicates expression of Pgp in the capillary endothelial cells of rat brain parenchyma. (C) Localization of MRP to epithelial cells of rat and human CP by immunohistochemistry. Rat-brain sections immunostained in the absence of primary mAb (a; ×100) and in the presence of mAb MRPr1 (b; ×100). Human CP tissue stained with mAb MRPr1 (c; ×400) and mAb QCRL-1 (d; ×400).