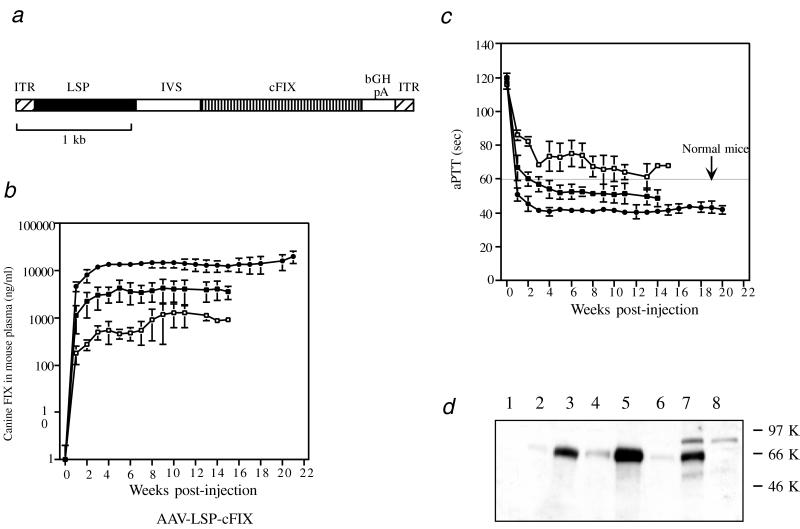
Figure 1.
Long-term expression of functional canine factor IX in hemophilia B mice. (a) Schematic drawing of rAAV-LSP-cFIX vector. (b) ELISA assays. Recombinant AAV-LSP-cFIX was delivered as a single intraportal injection into the liver of adult hemophilic C57BL/6 mice in a dose of 2 × 1011 (n = 4, ■) or 5.6 × 1011 (n = 5, ●) vector genomes or into the liver of adult hemophilic 129 mice at a dose of 2 × 1011 particles (n = 3, □). Mice were bled weekly after vector administration. The canine factor IX concentration in the mouse plasma was determined by an ELISA assay. (c) Functional factor IX activity in the mouse plasma was determined by an in vitro aPTT assay (same symbols as in b). The line in the middle shows the aPTT for normal mice. (d) Western blot analysis. Plasma from C57BL/6 hemophilic mice 4 months postinjection with 2.8 × 1011 particles or 5.6 × 1011 particles of AAV-LSP-cFIX was analyzed by Western blotting. Lanes: 1, naive mouse, (0.1 μl of plasma); 2 and 3, plasma from mouse injected with 2.8 × 1011 particles (0.01 and 0.1 μl, respectively); 4 and 5, plasma from mouse injected with 5.6 × 1011 particles (0.01 and 0.1 μl, respectively); 6 and 7, normal canine plasma (0.01 and 0.1 μl, respectively) (Sigma); 8, 0.1 μl of plasma from a hemophilic dog (a gift from T. Nichols of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill).