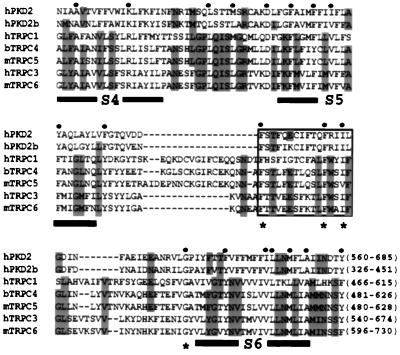
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of the TRP-like regions in human PKD2 (hPKD2, GenBank accession no. U50928), hPKD2b (AF092170), hTRPC1 (Z73903), bovine TRPC4 (bTRPC4, X99792) mouse TRPC5 (mTRPC5, AJ006204), hTRPC3 (Y13758), and mTRPC6 (U49069). The first and last amino acids of each sequence, numbered according to their corresponding cDNAs, are shown in the end of each sequence. Identical or similar substitutions (similar substitutions are grouped as follows: F and Y; I and V; R and K; L and M; or N, D, Q, and E) conserved in five or seven sequences are shown in gray or by a dot on top of the sequences, respectively. Low consensus shown in gray allows the identification of similar residues within the TRP family. Alignment was done according to hierarchical clustering using a blosum62 scoring table (35). Amino acid residues corresponding to putative TM segments (S3–S6) are underlined, and the boxed area shows a putative pore helical region (30). Asterisks denote conserved residues that may participate in the formation of the ion pore.