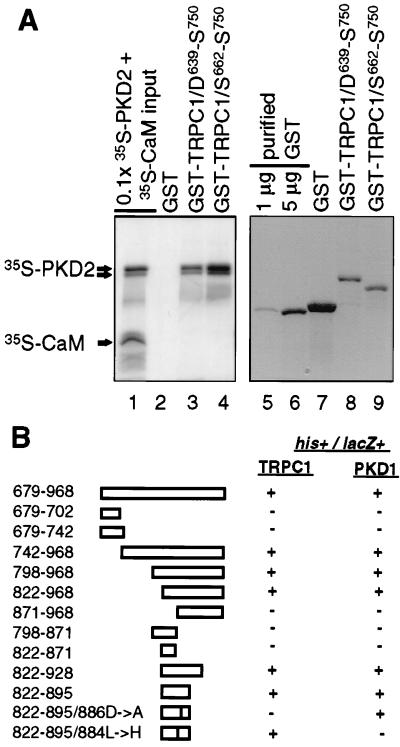
Figure 6.
Identification of the C-terminal interacting domain in PKD2. (A) Direct interaction between the C-terminal tail of PKD2 and TRPC1. In vitro column binding of 35S-PKD2 and 35S-CaM to GST-TRPC1/D639–S750 or GST-TRPC1/S662–S750 (lanes 1–4). Lane 1 shows 0.1× the input amount of 35S-PKD2 and 35S-CaM. Bound 35S-PKD2 and 35S-CaM to GST, GST-TRPC1/D639-S750, or GST-TRPC1/S662–S750 is shown in lanes 2–4 and the immobilized amounts of GST, GST-TRPC1/D639–S750, and GST-TRPC1/S662–S750 subjected to in vitro column binding are shown in lanes 7–9. To obtain an estimate of the immobilized amounts of GST, GST-TRPC1/D639–S750, or GST-TRPC1/S662–S750 used in the in vitro column binding assays, 1 or 5 μg of purified GST is shown in lanes 5 and 6. A lower molecular weight band corresponding to a C-terminal proteolytic product of 35S-PKD2 is shown by an arrow below the band corresponding to full-length 35S-PKD2. (B) cDNAs corresponding to the entire C-terminal cytoplasmic region of PKD2, systematic N- or C-terminal deletions of this region (amino acid residues 679–968) or nonconserved substitutions in the region 822–895 were tested for their interaction with the cytoplasmic tail of TRPC1 (D639–S750) or PKD1 (P4124–T4303) by the yeast two-hybrid assay. Positive interactions were scored for both survival in plates lacking histidine (his+) and production of β-galactosidase (lacZ+).